Tensorboard 可視化之圖層
Tensorflow 自帶的 tensorboard 可以構建我們的神經網絡圖層, 讓我們看看自己的神經網絡長什么樣.
開始構建圖層結構啦
我們要用到前面用到的代碼來構建神經網絡圖像
首先是數據的輸入 input :
# 我們先給輸入和輸出的占位符指定名稱
# 指定的名稱會在可視化的圖層 input 中顯示
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='x_in')
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='y_in')
圖層可以包含子圖層, 所以, 我們要用到 with tf.name_scope('inputs') 將xs和ys包含起來, 作為輸入層. (inputs 就是圖層的名字, 可任意命名)
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='x_in')
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='y_in')
接下來, 就是layer了, 我們前面用了add_layer函數來添加圖層, 這里我可以直接在add_layer函數里面構建圖層結構. ( 記得 name_scope 可以嵌套的哦
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
# 每一個圖層名為 `layer`
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
# 添加層里面的小部件也需要定義
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, )
return outputs
最后是loss和training部分了, 同樣為他們各自取名
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-prediction),
reduction_indices=[1]))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_setp = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
繪制我們的神經網絡圖啦
繪制方法為tf.summary.FileWriter(dir, sess.graph), 第一個參數為圖的儲存路徑, 第二個參數是將前面定義好的框架信息收集起來, 最后放到dir目錄中, 因此需要先獲得 Session
sess = tf.Session()
# 執行 python3 filename.py 之后會自動創建 graph 文件夾
# 並把生成的圖層圖像信息保存在 graph 下, 需要用瀏覽器觀看
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('graph/', sess.graph)
運行完整代碼后「[完整代碼] (#code)」, 會自動生成圖片信息並保存到 graph 目錄中, 然后什么在 graph 上一級目錄執行下面這條命令, 它會輸出一條地址, 我們在瀏覽器上打開http://127.0.1.6006:1
Ubuntu ~# tensorboard --logdir='./graph/'
Starting TensorBoard b'41' on port 6006
(You can navigate to http://127.0.1.1:6006)
...
這個網頁有多個選項卡, 因為我們只定義了sess.graph, 所以我們切換到GRAPH, 可以看到我們的神經網絡的基本結構
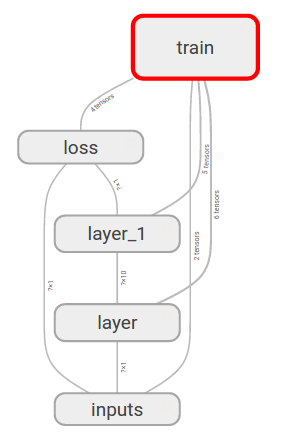
我們再點開inputs圖層看看, 里面有x_in和y_in兩個輸入, 這兩個名字是我們取的, 其他的可以自己看看啦

完整代碼
最后把輸入輸出圖層也加上了名字, 看下完整代碼
# !/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define add layer function.
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, )
return outputs
# Define palceholder for inputs to network.
# Use [with] including xs & ys:
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='x_in') # Add name
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='y_in')
# Add hidden layer
with tf.name_scope('hidden_layer'):
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
# Add output layer
with tf.name_scope('output_layer'):
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
# The error between prediction and real data
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-prediction),
reduction_indices=[1]))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_setp = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
sess = tf.Session()
# ** Add frame to file
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('./graph/', sess.graph)
# Important step
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
最后效果:

