宏觀流程如下圖:

client端
生成StreamGraph
env.addSource(new SocketTextStreamFunction(...))
.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction())
.keyBy("word")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.reduce(new ReduceFunction())
.print()
StreamExecutionEnvironment上的一系列api調用會在env->transformations中添加相應的StreamTransformation對象,然后調用StreamGraphGenerator->transformation方法遍歷所有的StreamTransformation對象生成最終的StreamGraph。
如上代碼段會生成如下StreamGraph:

StreamGraph->JobGraph
private List<StreamEdge> createChain(
Integer startNodeId,
Integer currentNodeId,
Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes,
List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes,
int chainIndex,
Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>>> chainedOperatorHashes)
從StreamGraph的所有sourceStreamNode開始遍歷處理,如果是可鏈接的(isChainable為true)則繼續,同時生成該節點的StreamConfig信息(包含StreamOperator``chainIndex``chainEnd等),否則生成新的JobVertex,最后鏈接connect函數創建JobEdge對象鏈接JobVertex。
public static boolean isChainable(StreamEdge edge, StreamGraph streamGraph) {
StreamNode upStreamVertex = edge.getSourceVertex();
StreamNode downStreamVertex = edge.getTargetVertex();
StreamOperator<?> headOperator = upStreamVertex.getOperator();
StreamOperator<?> outOperator = downStreamVertex.getOperator();
return downStreamVertex.getInEdges().size() == 1
&& outOperator != null
&& headOperator != null
&& upStreamVertex.isSameSlotSharingGroup(downStreamVertex)
&& outOperator.getChainingStrategy() == ChainingStrategy.ALWAYS
&& (headOperator.getChainingStrategy() == ChainingStrategy.HEAD ||
headOperator.getChainingStrategy() == ChainingStrategy.ALWAYS)
&& (edge.getPartitioner() instanceof ForwardPartitioner)
&& upStreamVertex.getParallelism() == downStreamVertex.getParallelism()
&& streamGraph.isChainingEnabled();
}
如上代碼會生成包含兩個JobVertex對象的JobGraph:

JobVertex的configuration屬性中的chainedTaskConfig_``chainedOutputs分別包含了該節點鏈接的所有StreamNode節點的配置信息和所有SteamNode本身序列化后的二進制數組
JobManager
主要把客戶端提交的JobGraph轉化成ExecutionGraph,並把ExecutionGraph包含的所有ExecutionVertex對應的Execution提交給分配到其執行所需資源的TaskManager
DistributionPattern分發模式用於確定生產者(產生中間結果IntermediateResultPartition)與其消費者(通過ExecutionEdge)怎樣鏈接
switch (channel.getShipStrategy()) {
case FORWARD:
distributionPattern = DistributionPattern.POINTWISE;
break;
case PARTITION_RANDOM:
case BROADCAST:
case PARTITION_HASH:
case PARTITION_CUSTOM:
case PARTITION_RANGE:
case PARTITION_FORCED_REBALANCE:
distributionPattern = DistributionPattern.ALL_TO_ALL;
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown runtime ship strategy: " + channel.getShipStrategy());
}
ExecutionVertex之間如何鏈接:
-
ALL_TO_ALL模式:
則每一個並行的ExecutionVertex節點都會鏈接到源節點產生的所有中間結果IntermediateResultPartition

-
POINTWISE模式:-
源的並行度和目標並行度相等。這種情況下,采用一對一的鏈接方式:

-
源的並行度小於目標並行度。這種情況下,對於每一個執行節點鏈接到的源的中間結果分區由如下公式計算得到:
sourcePartition = (int)subTaskIndex / (((float) parallelism) / numSources)
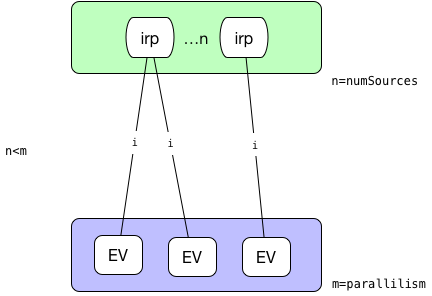 * 源的並行度大於目標並行度。這種情況下,計算每一個執行節點會平均鏈接到幾個源節點,平均分配后余下的都分給最后一個節點。 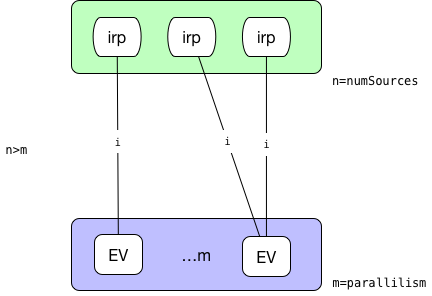 -
最后提交給TaskManager的TaskDeploymentDescriptor如下:

ResultPartitionDeploymentDescriptor有一個numberOfSubpartitions字段,其等於此ResultPartition的消費者的數量(被下級鏈接到的邊數),因為最終執行的時候每一個ResultPartition還會拆分為numberOfSubpartitions相同數量的ResultSubPartition。
InputGateDeploymentDescriptor包含多個InputChannelDeploymentDescriptor和一個用以指示消費第幾個ResultSubPartition的consumedSubpartitionIndex。每一個InputGateDeploymentDescriptor消費的所有ResultPartition的subPartitionIndex是一樣的。

例如並行度均為2的兩個ExecutionJobVertex采用ALL_TO_ALL方式鏈接的結果如下:

TaskManager
TaskManager接收到TaskDeploymentDescriptor對象后進行反序列化生成Task對象並進行一系列的初始化操作(如:根據ResultPartitionDeploymentDescriptor對象初始化writers[ResultPartitionWriter],根據InputGateDeploymentDescriptor初始化inputGates[SingleInputGate],重新設置classLoader等)然后啟用新線程執行invokable[AbstractInvokable]->invoke方法。
也就是說Task的主要業務邏輯其實都包含在了AbstractInvokable對象中,我們來具體看下其子類StreamTask(SourceStreamTask和OneInputStreamTask)
StreamTask的invoke方法會創建OperatorChain

重點關注chainEntryPoint這個屬性是BroadcastingOutputCollector類型,其collect方法如下:
public void collect(StreamRecord<T> record) {
for (Output<StreamRecord<T>> output : outputs) {
output.collect(record);
}
}
即使依次遍歷鏈中的每一個output進行collect操作,而其中的每一個output又是ChainingOutput及其子類。
@Override
public void collect(StreamRecord<T> record) {
if (this.outputTag != null) {
// we are only responsible for emitting to the main input
return;
}
pushToOperator(record);
}
protected <X> void pushToOperator(StreamRecord<X> record) {
try {
// we know that the given outputTag matches our OutputTag so the record
// must be of the type that our operator expects.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
StreamRecord<T> castRecord = (StreamRecord<T>) record;
numRecordsIn.inc();
operator.setKeyContextElement1(castRecord);
operator.processElement(castRecord);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExceptionInChainedOperatorException(e);
}
}
其中operator是OneInputStreamOperator類型其子類業務實現邏輯(processElement)方法:調用用戶自定義函數userFunction[Function]處理后按需調用output.collect(element)其中output可能也是一個ChainingOutput類型,這樣整個執行鏈路就被一級一級鏈接起來了。
this.chainEntryPoint = createOutputCollector(
containingTask,
configuration,
chainedConfigs,
userCodeClassloader,
streamOutputMap,
allOps);
if (headOperator != null) {
Output output = getChainEntryPoint();
headOperator.setup(containingTask, configuration, output);
}
對於StreamTask常見的一個子類SourceStreamTask,其run方法:
@Override
protected void run() throws Exception {
headOperator.run(getCheckpointLock(), getStreamStatusMaintainer());
}
對於OperatorChain鏈上最后一個operator其output為RecordWriterOutput類型其封裝了StreamRecordWriter配合ChannelSelector寫入到具體的某個ResultSubPartition
public void emit(T record) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (int targetChannel : channelSelector.selectChannels(record, numChannels)) {
sendToTarget(record, targetChannel);
}
}
常見的ChannelSelector:
RescalePartitioner|RebalancePartitioner: 輪詢KeyGroupStreamPartitioner: 基於key分組GlobalPartitioner: 全局,只通過subpartition==0ShufflePartitioner:隨機到子分區ForwardPartitioner: 本地轉發BroadcastPartitioner: 廣播到所有分區
另一個StreamTask常見的一個子類OneInputStreamTask,其run方法:
@Override
protected void run() throws Exception {
// cache processor reference on the stack, to make the code more JIT friendly
final StreamInputProcessor<IN> inputProcessor = this.inputProcessor;
while (running && inputProcessor.processInput()) {
// all the work happens in the "processInput" method
}
}
其inputProcessor是StreamInputProcessor類型,在init方法中創建
if (checkpointMode == CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE) {
long maxAlign = taskManagerConfig.getLong(TaskManagerOptions.TASK_CHECKPOINT_ALIGNMENT_BYTES_LIMIT);
if (!(maxAlign == -1 || maxAlign > 0)) {
throw new IllegalConfigurationException(
TaskManagerOptions.TASK_CHECKPOINT_ALIGNMENT_BYTES_LIMIT.key()
+ " must be positive or -1 (infinite)");
}
this.barrierHandler = new BarrierBuffer(inputGate, ioManager, maxAlign);
}
else if (checkpointMode == CheckpointingMode.AT_LEAST_ONCE) {
this.barrierHandler = new BarrierTracker(inputGate);
}
barrierHandler與設置的CheckpointingMode相關:
EXACTLY_ONCE:BarrierBufferAT_LEAST_ONCE:BarrierTracker
inputProcessor的processInput方法會調用barrierHandler.getNextNonBlocked()如果獲取到一條完整記錄則調用streamOperator.processElement(record)觸發整體調用鏈的執行。
