01|基於圖像的火焰檢測算法
-
數據集總共數量,包括的干擾,用來訓練的數量、用來測試的數量。
-
訓練測試結果
-
仿真實驗環境
-
指標公式
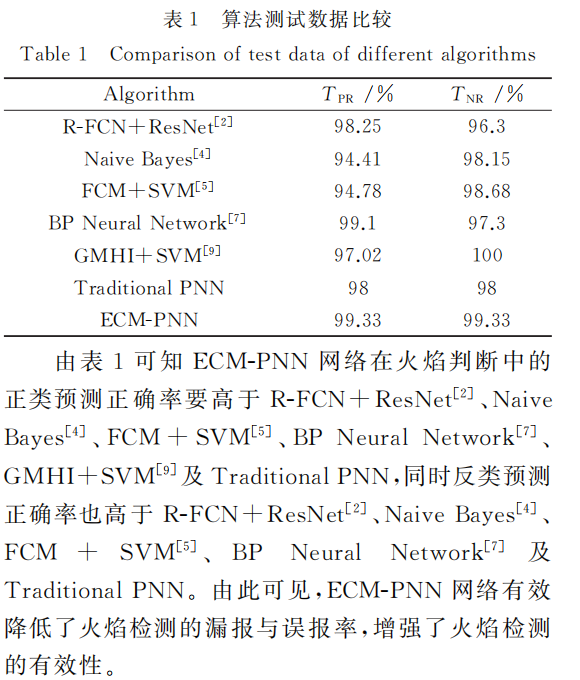
用正類預測正確率 \(\left(T_{\mathrm{PR}}\right)\) 與反類預測正確率\(\left(T_{\mathrm{NR}}\right)\) 來描述實驗結果的准確性,定義如下
\[T_{\mathrm{PR}}=\frac{T_{\mathrm{P}}}{T_{\mathrm{P}}+F_{\mathrm{N}}} \\ T_{\mathrm{NR}}=\frac{T_{\mathrm{N}}}{F_{\mathrm{P}}+T_{\mathrm{N}}} \]式中 \(: T_{\mathrm{P}}\) 表示預測結果為正類,實際上是正類 \(; F_{\mathrm{P}}\) 表示預測結果為正類,實際上是反類;FN 表示預測結 果為反類,實際上是正類;TN表示預測結果為反類, 實際上是反類。
-
算法結果比較
02|基於圖像處理的森林火險檢測系統
03|基於視頻圖像的火焰檢測
-
實驗環境
-
對比方法

-
實驗結論
特征提取的火焰區域更加完整,更加准確,但是背景差分將固定的圖像作為背景圖像時,周圍許多的環
境因素會不同程度上影響到檢測的准確性。實驗結果也表明,一般情況下自然環境中的火災重心高度系
數會隨着燃燒時間而變大,但是最大不會超過 0.45。
04| 基於計算機視覺的森林火災識別算法設計
-
試驗平台搭建
-
說明實驗設計

-
實驗結果
通過上述所設計的3組對照試驗,可以得出單純的采用一種特征對煙霧與火焰的判別有一定的准確度,但是精度不高。若利用圖像的綜合特征進行分類,試驗結果表明比采用單類特征的分類效果要好。由於林火行為的復雜性與特殊性,在火災初期通常是先產生煙霧,單一的采用火焰識別容易錯過撲滅最佳時機,故采用煙火綜合特征共同判斷森林火災,識別准確率可達97.82%。
通過比較容易得出,利用圖像綜合特征識別方法比采用單類特征識別效果更好,而且通常情況下使用的特征越多,分類效果越好,但是這並不絕對,還要根據所處環境、氣候以及識別對象綜合進行考慮,選取最優的特征組合從而得到更佳的試驗結果。
05|從傳統到深度:視覺煙霧識別、 檢測與分割
06|Using Popular Object Detection Methods for Real Time Forest Fire Detection
In this section, we will show experiments results through 3 object detection methods, Faster R-CNN, YOLO (tiny-yolo-voc1, tiny-yolo-voc, yolo-voc.2.0, and yolov3) and SSD.
For Faster R-CNN, we give a result based on 120000 iteration times. For YOLO, we find that YOLO has a bad performance on smaller cooler fire detection, so we try to adjust the structure of tiny-yolo-voc by adding two more layers (one is convolutional layer and the other is maxpooling layer, the filter of convolutional layer is 8). When training is finished, we finally find that these two added layer boost the original smaller fire detection accuracy rate. The experiment result proves that more layer with small filter catch more details. For SSD, we test its static and real-time detection accuracy rate on smaller fire, the result shows that this methods has better performance than YOLO (tiny-yolo-voc), it can make an accurate and real-time detection an smaller fire.
對比三種目標檢測方法 : Faster R-CNN YOLO SSD
Faster R-CNN的訓練輪數是120000
yolo在smaller cooler fire detection上表現不佳,在增加了一個八個濾波器的卷積層和一個最大池化層之后,原本的小火焰檢測准確率提高了。
實驗證明更多的層(因為其濾波器更多)可以捕獲更多的細節信息。
SSD的靜態和實時檢測准確率在小火焰的上比YOLO效果更好,更適合進行准確而實時的小火焰檢測
A. Faster R-CNN
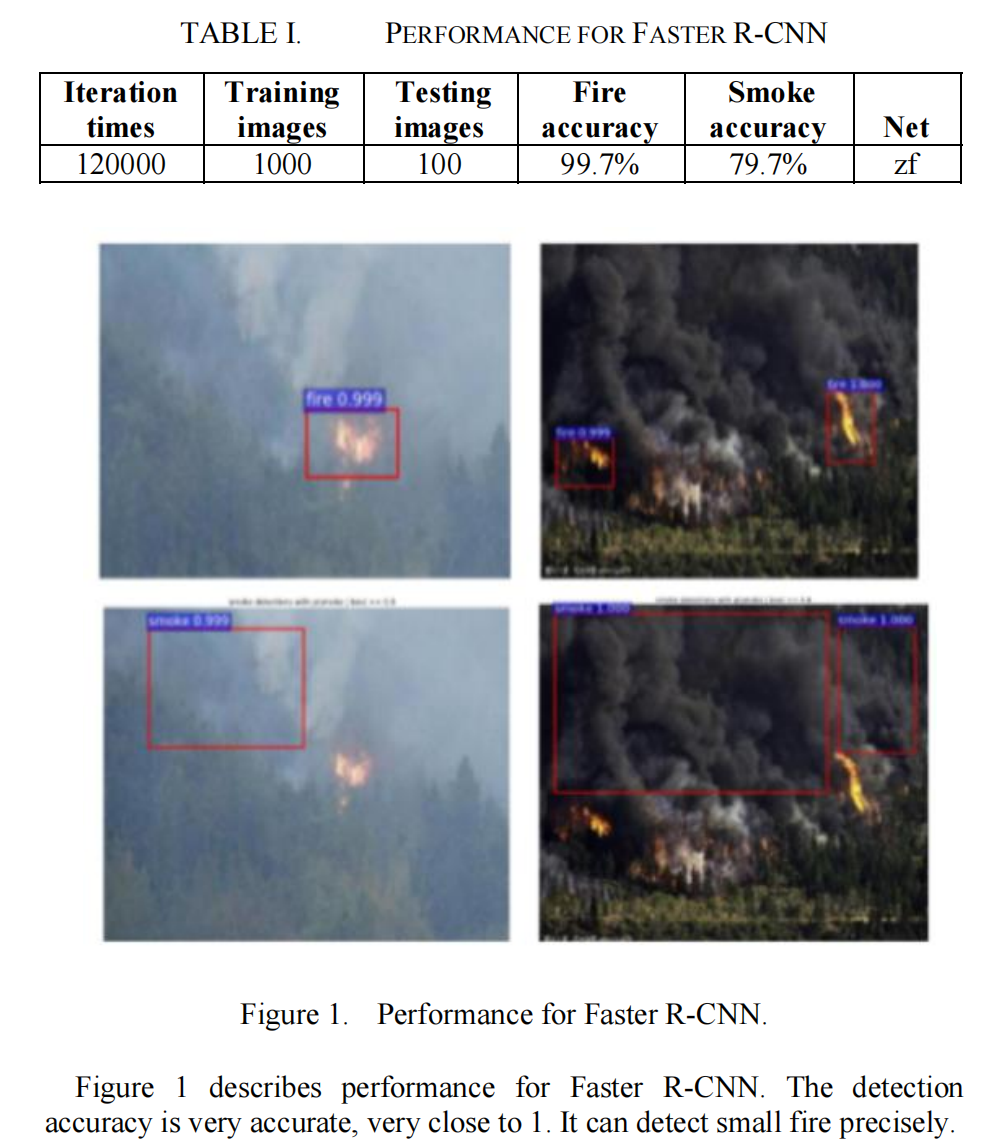
We use 1000 fire pictures with 300*300 size as benchmark. BBox-Label-Tool v2 is used to label the pictures, fire and smoke are both labeled therein. We alter the iterations for each training stage at 120000, 60000, 120000, and 60000 and keep the default values for all the other settings.
使用了300*300圖片大小的1000章火焰圖片作為Benchmark
標注圖片的工具是BBox-Label-Tool v2。 therein 其中標注了火焰和煙霧(smoke)
改變訓練輪數在120000,6000,同時保持其他的默認設置
Fire and smoke detection accuracy rate both are very good, even the very small fire Faster R-CNN can detect rightly. For smoke detection accuracy rate, Faster R-CNN is close to 1. For fire detection, detection accuracy rate for the small fire is 0.99 and the dark fire is 0.974. We only show static picture herein, because as the author of SSD said, it can only operates at only 7 frames per second (FPS), too slow for real-time fire-detection applications. We focus on research on YOLO and SSD, the later has higher FPS and can satisfy the real-time detection need. Table I describes performance for Faster R-CNN.
火焰和煙霧的檢測准確率都非常好,即使是非常小的火焰Faster R-CNN 都能正確地檢測。
對於煙霧檢測准確率,Faster R-CNN 接近1。對於火焰檢測,檢測准確率對於小火是0.99。對於暗火是0.974。
在此,僅展示靜態圖片,正如ssd的作者所說他只能在7FPS上運行,對於實時火焰檢測來說實在太慢。
我們重點研究YOLO和SSD,后者有更高的FPS而且可以滿足實時火焰檢測的需要。
B. YOLO
For YOLO, we test how different layers structure influence the accuracy rate. Still, we use 1000 pictures to make the fire/smoke datasets, the same datasets for those three object detection methods. We use the tiny-yolo-voc structure to train the datasets, finally find that when the iteration times equals to 120000 and learning rate is 0.01, this original structure has plain accuracy. We adjust the tiny-yolo-voc by adding two layers, which include 1 convolutional layer(the filter is 8) and 1 maxpooling layer, the results proves that this new structure improves both fire and smoke detection accuracy. Even we train the yolo-voc.2.0, this new structure still shows better performance. But in the end, yolov3 performs better. When we train the original tiny-yolo-voc, we initialize the images size as 416*416, during the experiments, we find that when the image size is set as 608*608, the performances become better. So next when we train yolo-voc.2.0 and tiny-yolo-voc1, we both initialize the image size at 608*608. When we utilize tiny-yolo-voc1 to train fire only, it performs best. But when the new class smoke is added, the fire accuracy decrease 10%. When we train dataset using yolov3, we finally find that this configuration performs best. Herein single training means fire training, combine training means fire/smoke joint training. Figure 2 shows performance for YOLOv3. YOLOv3 has a bad performance for small fire.
我們測試了不同的網絡層結構如何影響准確率。盡管如此,我們還是使用了1000張圖片來制作火災/煙霧數據集,這三個目標檢測方法的數據集是相同的。
我們用tiny-yolo-voc 結構,來訓練數據集,最終發現當訓練輪數等於120000而學習率是0.01時,該原始結構具有較好的(plain 朴素 簡單的)准確率
通過增加兩個層(8個濾波器的卷積層和一個最大池化層)調整tiny-yolo-voc,這種結構會同時提高火焰和煙霧的准確率。
yolo voc.2.0 依然比改進之后的tiny-yolo-voc效果差。但是yolo v3就要比改進之后的tiny-yolo-voc效果好了。
當我們訓練原始tiny yolo voc 時,初始化圖片大小是416*416,在實驗過程中,我們發現當圖片大小是 608*608時,訓練效果會變得更好。
當我們利用(utilize)tiny-yolo-voc1 只訓練火焰,效果是最好的。
但是新的類別,煙霧,加進來時,火焰准確率就下降了10%。


C. SSD
In this section, we use SSD 300*300 model to train our fire datasets. The resized width and resize height are both 300, the batch size equals to 1, number of the testing images equals to 342 and number of the training image is 668, the iteration times is 120000. When the training ends, we finally find that the fire detection accuracy for 100 images is up to 1, except one very small fire which equals to 0.58. For smoke detection, accuracy of in 100 test images are 0, but 13 in 27 are no smoke images, so the missing detection rate is 14 percent. The smoke accuracy rate of these remain 73 images are up to 97.88 percent.
這節描述的是SSD300的模型。
圖片被resize到300*300,batch size設置為1,訓練集是668張,測試集是342張,訓練輪數是120000。
火焰准確率達到了1,除了非常小的火焰約等於0.58。對於煙霧檢測,除了沒有煙霧的圖片集,其余的達到了97.88%的准確率

D. Area changes
For false detection, we think area changes detection helps a lot. When the fire is bigger and bigger, the area of the fire is growing. The SSD can detect the area of the fire by four value, Xmin, Ymin, Xmax and Ymax. These four values present the coordinates of the top left corner and the coordinates of the lower right corner, then we calculate the area very easily. We catch the two interval frame of the fire usually, when the area grows bigger, this must be the fire.
對於錯誤檢測,我們認為面積變化會有所影響。當火焰越來越大,這個區域的火焰在生長。SSD可以檢測到火焰通過值,最小值,最大值。這4個值分別表示左上角的坐標和右下角的坐標( coordinates ),然后我們非常容易計算出面積。我們可以通過火的兩個區間(interval)框架( frame),當區域變大,肯定就是火。
07|A convolutional neural network-based flame detection methodin video
The proposed algorithm based on convolutional neural network (CNN) is implemented in C language and Caffe model on a standard desktop PC which is equipped with a Octa-Core, CPU 3.6 GHz and 8 GB RAM. The flowchart of the method is shown in Fig. 2b.
這個建議的算法是基於CNN卷積神經網絡通過c語言和caffe實現的,
在xx的電腦配置上。
流程圖是Fig . 2b.
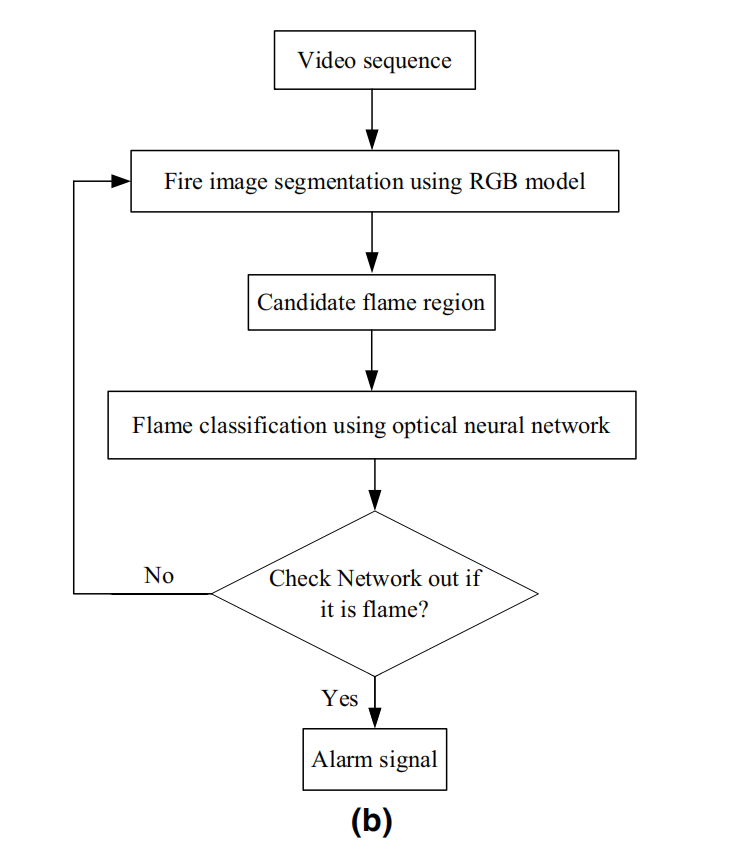
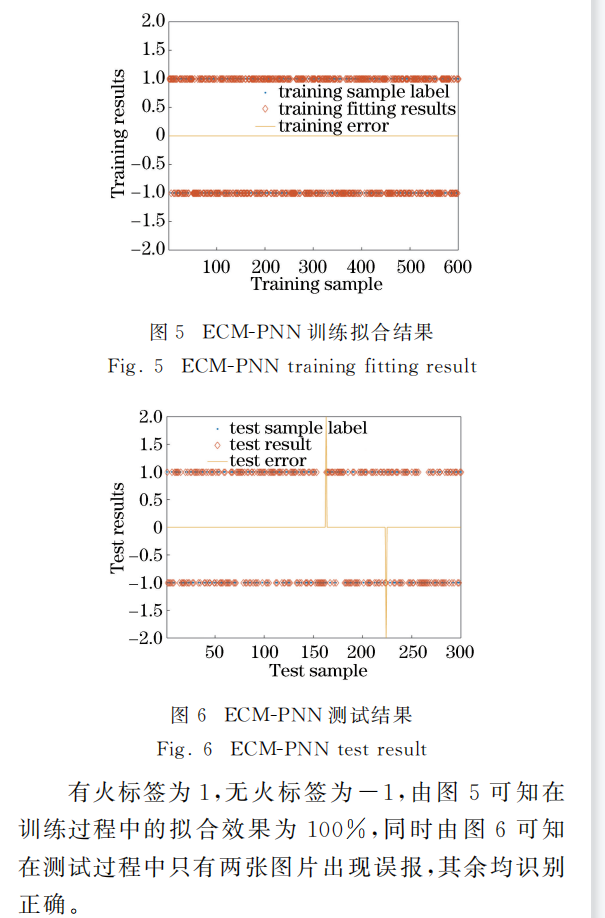
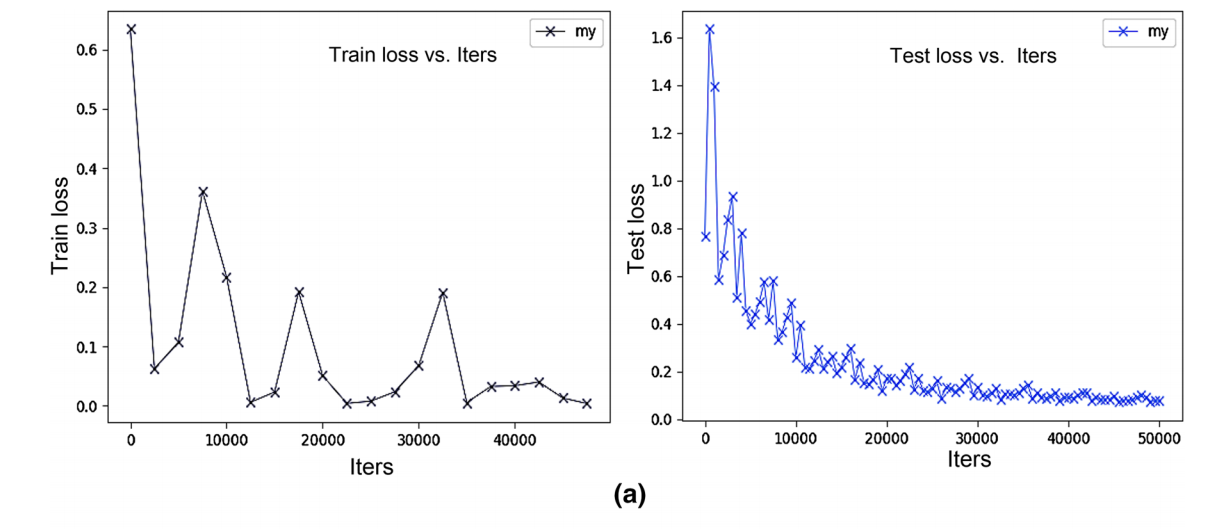
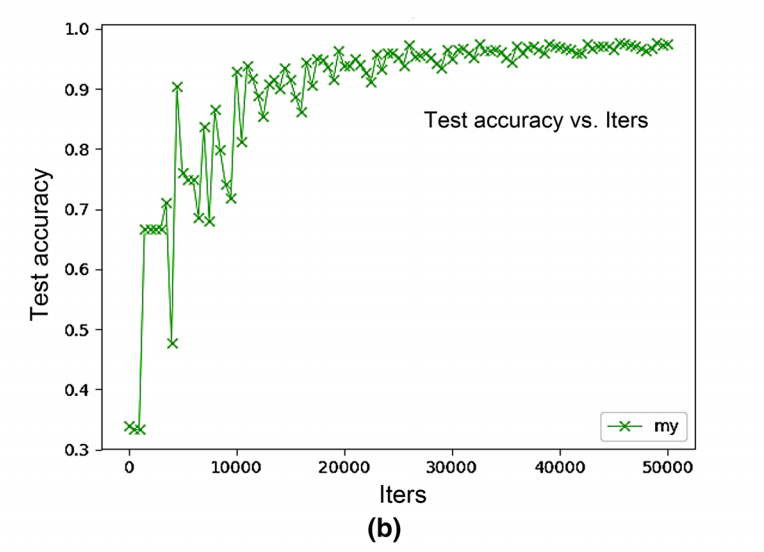
In the processing of training neural network model, the training of convolutional layer is to train some convolutional filters, which have high activation of the unique mode to achieve the purpose of CNN. The more convolutional layers, the more complicate features. In this paper, to train the better convolutional kernels and obtain the more effective combination mode of these convolutional kernels, the optimal parameters are obtained by the proposed model, and then test samples are effectively classified by optimal parameters. The loss function curve of train set and test set are shown in Fig. 5a. From this curve, we can see that as the number of training and testing iterations increases, the loss functions all decrease and then the curves tend to stabilize. The test accuracy curve is shown in Fig. 5b. From this curve, we can see that as the number of training iterations increases, the test accuracy improves and then the curve reaches highest accuracy which is 97.64% when the number of iterations is 50,000.
訓練神經網絡模型的過程中,卷積層的訓練是去訓練卷積核(卷積濾波器),其具有高度激活(activation)的獨特模式(unique mode)達到CNN的目的(獲取圖像特征?)。
在本文中,為了訓練出更好的卷積核並且獲得這些卷積核更有效的組合模式(combination mode),
在建議模型中獲得了優化參數,測試樣本被有效優化參數地分類。(通過提出的模型得到最優參數,然后通過最優參數對測試樣本進行有效分類。)訓練集和測試集的損失函數曲線(curve)如圖5a
通過這個曲線,我們可以知道,隨着訓練和測試的輪數增加,損失函數都遞減,而且曲線都趨於平滑。
fig 5b 顯示了測試准確率曲線。根據這個曲線,我們可以知道,隨着訓練輪數的增加,這個測試准確率在增強,並且在訓練到50000輪時,准確率達到了97.64%。
In the previous studies [16, 34], different color spaces were used to extract flame color features, these methods have achieved good results. However, the processes of color space transformation and feature extraction are too complicated to meet the real-time requirements. Due to the high intensity of the flame area based on near-infrared image, the researchers present a lot of fire detection algorithms based on near-infrared image [35, 36]. The methods reduce the highlighted interference and obtain better results, but the requirement of hardware equipment is higher. According to the advantages of flame detection based on near-infrared video images, the researchers proposed a dual-spectrum flame feature detection method [37, 38], which combines the flame features of visible video images with the flame features of near-infrared video images. This method can effectively eliminate the small hole phenomenon in the segmentation area.
在先前的研究中,不同的顏色空間被用來獲取火焰顏色特征(flame color features),這些方法已經達到了很好的實驗結果。
然而,這個 顏色空間轉換和特征提取的過程非常難以達到實時的需求。
由於基於近紅外圖像(near-infrared )的火焰區域強度(intensity )較高,研究者提出了很多基於近紅外圖像(near-infrared)的火災檢測算法[ 35,36 ]。
這種方法減少突出干擾(highlighted interference ),會獲得更好的效果,但是對硬件需求會更高。
根據基於近紅外視頻圖片優點進行火焰檢測,研究者提出了雙光譜(dual-spectrum)火焰特征檢測方法,其結合了可視化視頻圖像和近紅外視頻圖像的火焰特征。根據基於近紅外視頻圖像的火焰檢測的優點,研究人員提出了一種將可見光視頻圖像的火焰特征與近紅外視頻圖像的火焰特征相結合的雙光譜火焰特征檢測方法[ 37,38 ]。
這種方法可以有效地消除(eliminate)分割區域的小洞現象。該方法能有效消除(eliminate)分割區域中的小孔現象。
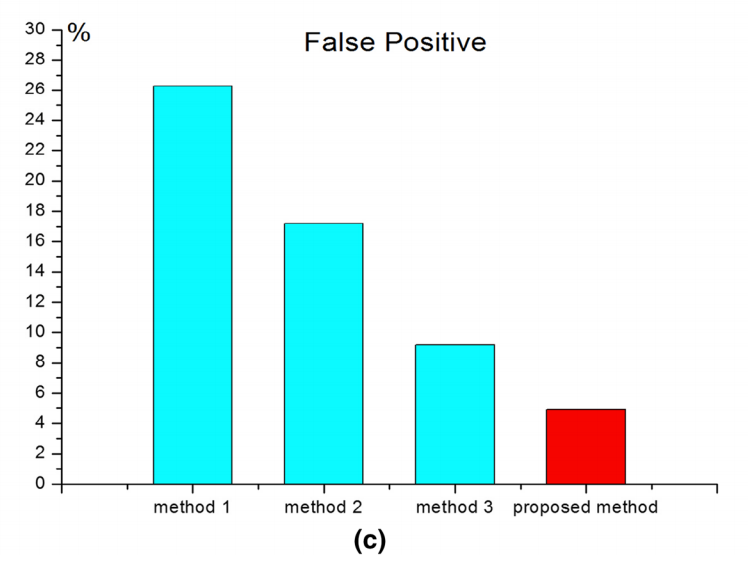
To evaluate the performance of the proposed method, experimental results were compared with obtained by the flame detection methods in the same scene, as shown in Fig. \(5 \mathrm{c}\). The first recognition method is based on color video image. The color model is used in our previous study and shown as:
\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}0<R-G<120 \\ 60<R-B<160 \\ 10<G-B<120\end{array}\right.\)
Here, R, G and B represent the value of R channel, Gchannel andB channel, respectively. The thresholds are determined by empirical values.
為了評估這些方法的性能,實驗結果將在同一場景下和獲取火焰檢測方法進行比較,如圖Fig.5c。第一個方法是基於視頻圖像顏色的。顏色模型在我們之前的研究中被表示為:
RGB顏色分別代表不同顏色通道,分別(respectively)。
閾值是通過經驗值確定的。
The second recognition method is based on near-infrared video image, and the flame area is extracted by the regional growth algorithm [39], which is suitable for flame segmentation. The selection regulation of pixel is shown as:
Here, \(R_{1}(x, y)=\left\{\begin{array}{l}1, f(x, y) \geq T_{\text {gray }} \\ 0, \text { otherwise }\end{array}\right.\), \(R_{2}(x, y)=\left\{\begin{array}{l}1,\left|f_{t}(x, y)-f_{t-1}(x, y)\right| \geq T_{m} \\ 0, \text { otherwise }\end{array}\right.\),\(T_{gray}\) denotes the threshold of pixel intensity, \(f_{t}(x, y)\) and \(f_{t-1}(x, y)\) denote video images at \(t\) and \(t-1\), respectively, \(T_{m}\) denotes the threshold of frame difference between \(f_{t}(x, y)\) and \(f_{t-1}(x, y)\). Then, the four-neighborhood growth mode is adopted to obtain the whole area of flame.
第二種識別( recognition)方法是基於近紅外視頻圖像,通過區域生長算法提取火焰區域,適合於火焰分割。這個選擇規則像素值被表示為:
其中,\(T_{gray}\)表示( denotes)像素強度閾值(threshold)。
\(T_{m}\) 表示火焰閾值差別在 \(f_{t}(x, y)\) 和 \(f_{t-1}(x, y)\)之間的。
然后, 整個火焰區域會被四領域生長模型采用。然后,采用四鄰域生長模式獲得整個火焰區域。
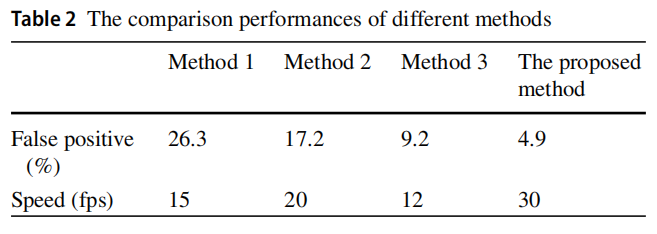
The third recognition method is used in our previous study which combines the first two methods, and the last method is proposed method. However, flame detection rates of first three methods are quite lower than the proposed detection rate. The comparison of computation speed of different methods is present in Table 2.
第三種識別方法會被我們之前的研究方法結合了前兩種方法,最近的方法被建議方法。但是,前3種方法的火焰檢測率都相當低於本文提出的檢測率。不同方法的計算速度比較見表2。