本篇解題記錄題源來自 AcWing 的 Summer 每日一題
補題鏈接:Here
2021/07/01 done
Week 1
星期一 AcWing 3485. 最大異或和 (Hard
思路
先求出前i個數的異或和sum[i],再在大小為m的滑動窗口內進行trie.

- \(\mathcal{O}(nlog\ n)\)
int n, m;
const int N = 31e5 + 10; //最多有n*31
int p[N][35], ct[N], idx; //ct[n]的作用是標記滑動窗口內0,1的數量
int sum[100010]; //sum[i]存前i個數的異或和
void insertt(int u, int c) {
int t = 0;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {
int x = u >> i & 1;
if (!p[t][x]) {
p[t][x] = ++idx;
}
t = p[t][x];
ct[t] += c; //標記這里(有或刪除)一個數可以達到該位置
}
}
int query(int u) {
int t = 0;
int res = u;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {
int x = u >> i & 1;
if (ct[p[t][!x]] > 0) { //當x對面的那個數!x存在時(0,1)
x = (x + 1) % 2; //x就變成另外一個數 !x
}
res ^= x << i;
t = p[t][x];
}
return res;
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
int t;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> t;
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] ^ t; //sum[i]表示前i個數的^
}
insertt(0, 1); //插入0,是為了方便前m個數進行異或得出的答案可以是它本身的值
int res = 0; //求最大值
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i > m) insertt(sum[i - m - 1], -1); //將滑動窗口外的數除去,這時就要修改ct,故-1
res = max(res, query(sum[i])); //在滑動窗口內求最大值
insertt(sum[i], 1); //求完后記得插入該值,方便后面的值進行異或
}
cout << res;
}
星期二 AcWing 3493. 最大的和 (Easy
對於 \(30\%\) 數據,可以開兩重 for 循環暴力找
但在 \(100\%\) 數據里肯定會 T
所以要用前綴和進行優化 (當然也可以用隊列優化,這里就不展開了,貼一個講解鏈接
- \(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
using ll = long long;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
ll a[N], s[N];
ll st[N];
void solve() {
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> st[i];
if (st[i]) s[i] += s[i - 1], sum += a[i]; // 如果是 st[i] = 1 的情況說明直接就可選,sum 累加即可
else
s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i]; // 需要轉換狀態的話則要利用前綴和累加了
}
ll res = 0;
for (int i = k; i <= n; ++i) res = max(res, s[i] - s[i - k]);
cout << res + sum;
}
星期三 AcWing 3499. 序列最大收益 (Mid
參考最長上升子序列
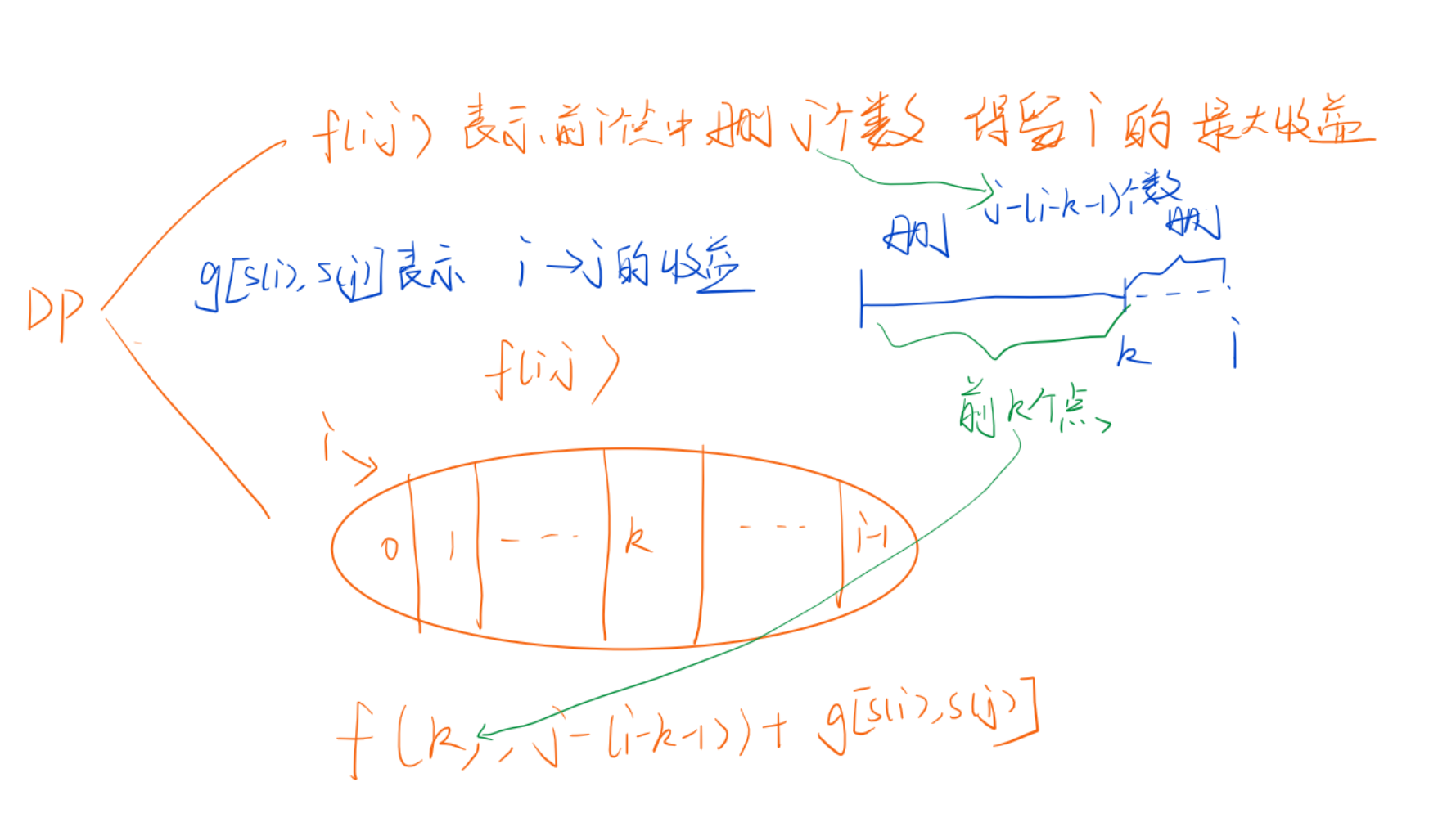
f[i][j]表示從0~i-1中刪j個點后,0~i的收益最大值- 或者說成前i個點中刪j個數,保留i的最大收益
- 按i來划分集合,可以划分為0~i-1,其中0就代表前0個點刪j個數,等價於不刪.
- f[i][j]可以從f[u][?]轉移過來,我們對f[i][j]做一個轉換
- 既然要刪j個數,可以先把后面[u+1,i-1]給刪了,這樣會刪除i-1-u個數
- 然后再在前面[0,u]中刪j-(i-1-u)個數,此時u點和i點臨近,可加貢獻
w[a[u]][a[j]]
故可以得到如下狀態轉移方程f[i][j] = max(f[i][j],f[u][j-(i-u-1)]+w[a[u]][a[i]]);
const int N = 210;
int n, k, m;
int a[N]; // 記錄元素
int w[N][N]; // w[i][j]表示i->j的收益
int f[N][N]; // f[i][j] 表示0~i-1中刪除j個點后,0~i的最大收益
void solve() {
cin >> n >> k >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
cin >> w[i][j];
memset (f, -0x3f, sizeof (f) );
f[1][0] = 0; // init
// 第1個點刪0個數保留1的收益為0
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j <= k; j ++ ) //j從0~k,不刪就是0
for (int u = 1; u < i; ++ u) //最多刪i-1個
if (j >= i - u - 1) //注意是>=,=的條件下就說明既可以把后面刪完,也可以直接分配到0~i中
//故要計算狀態
f[i][j] = max (f[i][j], f[u][j - (i - u - 1)] + w[a[u]][a[i]]);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) ans = max (ans, f[m][i]);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
星期四 AcWing 3502. 不同路徑數
這道題,爆搜 + set去重即可
const int N = 10;
int n, m, k;
int e[N][N];
set<int>S;
int dx[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int res = 0;
void dfs(int sx, int sy, int u, int s) {
if (u == k) {
if (!S.count(s)) ++res, S.insert(s);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int x = sx + dx[i];
int y = sy + dy[i];
if (x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > m)continue;
dfs(x, y, u + 1, s * 10 + e[x][y]);
}
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
cin >> e[i][j];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
dfs(i, j, 0, e[i][j]);
}
cout << res;
}
星期五 AcWing 3510. 最長公共子序列 (Mid
const int N = 1e6 + 7;
int id[N], q[N];
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
memset(id, -1, sizeof(id));
for (int i = 0, x; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> x;
id[x] = i;
}
int tt = 0;
q[0] = -1;
for (int i = 0, x; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> x;
int k = id[x];
if (k == -1)continue;
int l = 0, r = tt;
while (l < r) {
int mid = l + (r + 1) >> 1;
if (q[mid] < k)l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
q[r + 1] = k;
tt = max(tt, r + 1);
}
cout << tt << '\n';
}
星期六 AcWing 3489. 星期幾 (Easy)
套公式,或者逐年累加
int Day(int y, int m, int d) {
if (m == 1 || m == 2) m += 12, y -= 1;
return (d + 2 * m + 3 * (m + 1) / 5 + y + y / 4 - y / 100 + y / 400 +
1) % 7;
}
string D[] = {
"January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"
};
string DD[] = {
"Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"
};
void solve() {
int y, d, mm;
string m;
while ( cin >> d >> m >> y) {
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i)
if (m == D[i])cout << DD[(Day(y, i + 1, d))] << "\n";
}
}
星期日 AcWing 3481. 階乘的和
using ll = long long;
int fact[20];//10!就大於1e6
int combin[4100];//存所有階乘能組合出來的數,0~10有11種階乘,2^11空間存儲
int m = 0;
void dfs(int u, int st) {
if (u == 11) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; ++i) {
if (st >> i & 1) {
res += fact[i];
}
}
combin[m++] = res;
return;
}
dfs(u + 1, st);
dfs(u + 1, st | 1 << u);
}
void solve() {
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
dfs(0, 0);
sort(combin, combin + m);
// m = unique(combin, combin + m) - combin; // 去重,可有可無
int x;
while (cin >> x, x >= 0) {
int l = 1, r = m - 1;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
//二分查找預處理數組
while (l < r) {
mid = l + r >> 1;
if (combin[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << (combin[l] != x ? "NO\n" : "YES\n");
}
}
Week 2
星期一 AcWing 3516. 最大面積 (Hard
第一眼看過去像二維前綴和問題,但實際要使用單調棧解決
下面給出 4 道相關知識點遞增的題目
830.單調棧 -> 131. 直方圖中最大的矩形 -> 152. 城市游戲 -> 3516. 最大面積
Y總視頻講解,建議直接空降 30 min
const int N = 2010;
char g[N][N];
int l[N], r[N], q[N];
int U[N], D[N], L[N], R[N];
int s[N][N];
int n, m;
int calc(int h[], int n) {
h[0] = h[n + 1] = -1;
int tt = 0;
q[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
while (h[q[tt]] >= h[i]) tt -- ;
l[i] = q[tt];
q[ ++ tt] = i;
}
tt = 0;
q[0] = n + 1;
for (int i = n; i; i -- ) {
while (h[q[tt]] >= h[i]) tt -- ;
r[i] = q[tt];
q[ ++ tt] = i;
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
res = max(res, h[i] * (r[i] - l[i] - 1));
return res;
}
void init() { // 注意初始化別寫錯...
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { // 枚舉行
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
if (g[i][j] == '1')s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] + 1;
else s[i][j] = 0;
U[i] = max(U[i - 1], calc(s[i], m));
}
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
for (int i = n; i; i--) { // 枚舉行
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
if (g[i][j] == '1')s[i][j] = s[i + 1][j] + 1;
else s[i][j] = 0;
D[i] = max(D[i + 1], calc(s[i], m));
}
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) { // 枚舉列
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (g[j][i] == '1') s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] + 1;
else s[i][j] = 0;
L[i] = max(L[i - 1], calc(s[i], n));
}
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
for (int i = m; i; i -- ) { // 枚舉列
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (g[j][i] == '1') s[i][j] = s[i + 1][j] + 1;
else s[i][j] = 0;
R[i] = max(R[i + 1], calc(s[i], n));
}
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)scanf("%s", g[i] + 1);
init();
int _;
cin >> _;
while (_--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y, x++, y++;
cout << max(max(U[x - 1], D[x + 1]), max(L[y - 1], R[y + 1])) << "\n";
}
}
星期二 AcWing 3404. 誰是你的潛在朋友
按題意來,把看同一本書的人放進數組。
意外的簡單
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
bool vis[n + 1] = {false};
int b[n + 1];
vector<int>a[m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> b[i];
a[b[i]].push_back(i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (a[b[i]].size() == 1)cout << "BeiJu\n";
else cout << a[b[i]].size() - 1 << "\n";
}
}
星期三 AcWing 3483. 2的冪次方
這道題,本質是對在二進制下的1進行遞歸處理
int n;
string dfs(int n) {
string str;
for (int i = 20; i >= 0; --i) {
int f = 1 << i;
if (i > 2 and (n & f)) {
str += "2(";
str += dfs(i);
str += ')';
n -= f;
if (n != 0) str += '+';
} else if (i <= 2 and (n & f)) {
if (i == 0)str += "2(0)";
if (i == 1) str += "2";
if (i == 2) str += "2(2)";
n -= f;
if (n != 0) str += '+';
}
}
return str;
}
void solve() { while (cin >> n)cout << dfs(n) << "\n";}
// 簡化代碼
string dfs(int x) {
if (!x)return "0";
string ans = "";
for (int j = 31; j >= 0; --j) {
if ((x >> j) & 1) ans += (j == 1) ? "2+" : "2(" + dfs(j) + ")+";
}
return ans.substr(0, ans.size() - 1);
}
void solve() {
int n;
while (cin >> n)cout << dfs(n) << "\n";
}
星期五 AcWing 3333. K-優字符串
int Case = 1;
void solve() {
int n, k, sum = 0;
cin >> n >> k;
string s;
cin >> s;
int l = 0, r = s.size() - 1;
while (l < r) {
if (s[l] != s[r])sum++;
l++, r--;
}
cout << "Case #" << Case++ << ": " << abs(sum - k) << "\n";
}
Week 3
星期一 AcWing 3554. 二進制
解法一: 模擬,二進制累加,當存在溢出時,即最后 c = 1 時要多輸出一個 1
void solve() {
string a, b;
cin >> a, b = a;
int c = 0;
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i -= 1) {
int tmp = (a[i] - '0') + c;
if (i == 31)tmp++;
a[i] = (tmp % 2) + '0';
c = tmp / 2;
}
if (c) cout << c;
cout << a << "\n";
c = 0;
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i -= 1) {
int tmp = (b[i] - '0') + c;
if (i == 31 || i == 30)tmp++;
b[i] = (tmp % 2) + '0';
c = tmp / 2;
}
if (c)cout << c;
cout << b << "\n";
}
解法二:轉換成 long long 計算
using ll = long long;
void f(ll n) {
if (n >> 32 & 1)cout << 1;//最大的32位加3會變成33位,檢查一下
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i -= 1) {
if (n >> i & 1)cout << 1;
else cout << 0;
}
cout << "\n";
}
void solve() {
string s; cin >> s;
ll n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i)
if (s[i] == '1')
n = n | (1ll << (31 - i));
f(n + 1), f(n + 3);
}
解法三:Python 不講武德
T = int(input())for _ in range(T):
n = int(input(),2)
print(bin(n+1)[2:].rjust(32, '0'))
print(bin(n+3)[2:].rjust(32, '0'))
星期二 AcWing 3565. 完美矩陣
using ll = long long;
const int N = 110;
ll a[N][N];
vector<int>e[N][N];
void solve() {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)e[i][j].clear();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
cin >> a[i][j];
e[min(i, n - i + 1)][min(j, m - j + 1)].push_back(a[i][j]);
}
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
if (!e[i][j].size())continue;
sort(e[i][j].begin(), e[i][j].end());
int t = e[i][j][(e[i][j].size() + 1) / 2 - 1];
for (int k = 0; k < e[i][j].size(); ++k)
ans += abs(t - e[i][j][k]);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
星期三 AcWing 3574. 乘積數量
方案一:前綴和維護區間負數個數
看到求區間的問題,會想到前綴和優化
我們可以用前綴和維護 \([1,s_n]\) 區間內的負數個數(因為會影響乘積的正負號的只有負數)
則對於區間 \([s_l,s_r]=v\),若 \(v\) 是奇數,則表示該區間的乘積為負數,反之是正數
-
若\(s_r−s_{l−1}\)為奇數,則必定是 \(s_r\) 和 \(s_{l−1}\) 一奇一偶
-
若\(s_r−s_{l−1}\)為偶數,則必定是 \(s_r\) 和 \(s_{l−1}\) 都是偶數或都是奇數
於是我們可以從前往后便利一遍數組,求出前綴和分別為奇數和偶數的個數
然后是一個組合數的問題了,設前綴和為奇數的個數為 \(v_1\) ,前綴和為偶數的個數為 \(v_2\)
區間為正數的子區間個數為 \(C^1_{v1}+C^1_{v2}\)
區間為負數的子區間個數為 \(C^1_{v1}×C^1_{v2}\)
int n;
int s[N];
int s0, s1;
void solve() {
cin >> n;
s0 ++ ;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
int x;
cin >> x;
s[i] = s[i - 1] + (x < 0);
if (s[i] & 1) ++ s1;
else ++ s0;
}
cout << (LL)s0 * s1 << " " << (LL)s0 * (s0 - 1) / 2 + (LL)s1 * (s1 - 1) / 2 << endl;
}
方案二:DP
DP[i] 表示以 i 結尾的區間有多少個含奇數個負數
- 則若 xs[i] < 0,則接到 i - 1 含偶數個負數的區間上
- 否則,則接到 i - 1 含奇數個負數的區間上
但容易發現 \(dp_i\) 僅和前一項相關,所以采用滾動數組
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N], c[2];
ll cnt0, cnt1;
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
int v = 1;
c[v]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (a[i] < 0) v ^= 1;
cnt0 += (ll)c[v];
cnt1 += (ll)c[v ^ 1];
c[v]++;
}
cout << cnt1 << " " << cnt0 << '\n';
}
星期四 AcWing 3580. 整數配對
沒什么好講的,排序,累加即可
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
int a[n + 1], cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i += 2)cnt += a[i] - a[i - 1];
cout << cnt ;
}
星期五 AcWing 3583. 整數分組
先對數組按升序排序,然后記錄每個數符合條件的最左側點下標,然后再用DP優化
- \(f(i,j) = max(f(i,j),f(L_i-1,j-1) + i - L[i] + 1)\)
輸出 \(f[n][k]\) 即可
const int N = 5e3 + 10;
int f[N][N], n, a[N], L[N], k;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int p = i;
while (p > 1 && a[p - 1] >= a[i] - 5) p--;
L[i] = p;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; ++j)f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
for (int j = 1; j <= k; ++j)
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[L[i] - 1][j - 1] + i - L[i] + 1);
}
cout << f[n][k] << "\n";
}
Week 4
星期三 AcWing 3617. 子矩形計數
簡單的前綴和累加
using ll = long long;
ll a[40001], b[40001], n, m, i, j, k, ans = 0;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> a[i]; if (a[i]) a[i] += a[i - 1];}
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {cin >> b[i]; if (b[i]) b[i] += b[i - 1];}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (k % i == 0) {
ll u = i, v = k / i, x = 0, y = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) if (a[j] >= u) x++;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) if (b[j] >= v) y++;
ans += x * y;
}
cout << ans;
}
星期四 AcWing 3624. 三值字符串
利用雙指針維護最小長度
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
void solve() {
string s; cin >> s;
int cnt[4] = {0};
int l = 0, ans = inf;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)s.size(); ++i) {
cnt[s[i] - '0']++;
while (cnt[1] and cnt[2] and cnt[3]) {
cnt[s[l] - '0']--;
ans = min(ans, i - l + 1);
++l;
}
}
cout << (ans == inf ? 0 : ans) << "\n";
}
星期五 AcWing 3629. 同心圓塗色
模擬即可,注意 PI 的取值
const double pi = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795;
bool cmp(int a, int b) {return a > b;}
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
int r[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)cin >> r[i];
sort(r, r + n, cmp);
double ans = 0.0;
int i;
for (i = 1; i < n; i += 2) {
ans += pi * (r[i - 1] * r[i - 1] - r[i] * r[i]);
}
if (i == n)ans += pi * r[i - 1] * r[i - 1];
printf("%.06lf", ans);
}
Week 5
星期一 AcWing 3636. 數組延伸
const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll n, x;
ll a[N];
void solve() {
cin >> n >> x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)cin >> a[i];
ll sum = 0, psum = 0;
//分別代表一開始的數組和,可以向外擴展最小次數的那個數之前的和
int cnt = N;
//最小向外拓展次數
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
sum += a[i];
int c = 0;
for (int j = a[i]; j % x == 0; j /= x)c++;
if (c < cnt)cnt = c, psum = sum - a[i];
}
//答案就是一開始的數組和加上向外拓展次數*數組和,再加上截止到向外拓展次數最小的那個數之前的和(到這個數開始,就不是完整的拓展了)
cout << sum * (cnt + 1) + psum << endl;
}
星期二 AcWing 3646. 分水果
最少 (0,0,1) 、(0,1,0)、(1,0,0),至多 (1,1,1)
所以特判情況即可
void solve() {
int a[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)cin >> a[i];
int ans = 0;
if (a[0])ans++, a[0]--;
if (a[1])ans++, a[1]--;
if (a[2])ans++, a[2]--;
sort(a, a + 3);
if (a[2] and a[1])ans++, a[2]--, a[1]--;
if (a[2] and a[0])ans++, a[2]--, a[0]--;
if (a[0] and a[1])ans++, a[0]--, a[1]--;
if (a[0] and a[1] and a[2])ans++;
cout << ans << "\n";
}
星期三 AcWing 3655. 樓層
數學 or 模擬
void solve() {
int n, x;
cin >> n >> x;
if (n <= 2)cout << 1 << "\n";
else cout << (n - 2 + x - 1) / x + 1 << "\n";
// cout << ((n-3)/x+2) << endl;
}
星期五 AcWing 3664. 數組補全
貪心
找比y小的個數,一定不能超過中位數位置,然后左置1,右置y
void solve() {
int n, k, p, x, y, tot = 0, a, d = 0, i = 0, l, m;
cin >> n >> k >> p >> x >> y;
for (; i < k; tot += a, d += (a < y), i++)cin >> a;
l = n / 2 - d < n - k ? n / 2 - d : n - k;
m = n - k - l;
if (l < 0 || tot + l + m * y > x)cout << -1;
else {
while (m--)cout << y << ' ';
while (l--)cout << 1 << ' ';
}
}
Week 6
星期一 AcWing 3672. 數組重排
i - a[i] != j - a[j]
等價於 i - j != a[i] - a[j]
只需要逆序排列即可
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n);
for (int &x : a)cin >> x;
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), greater<int>());
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << '\n';
}
星期二 AcWing 3679. 素數矩陣
4 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 4 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 4 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 4 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 4 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 4 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 4
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == j)cout << 4 << " ";
else if (j == i + 1) cout << 1 << " " ;
else if (i == n - 1 && j == 0) cout << 1 << " ";
else cout << 0 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
星期三 AcWing 3686. 移動序列
定位區間,然后計算1,0個數
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n);
int cnt1 = 0;
for (int &x : a) {
cin >> x;
if (x == 1)cnt1++;
}
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
while (a[i] == 0) i++; //第一個1的位置
while (a[j] == 0) j--; //最后一個1的位置
cout << j - i + 1 - cnt1 << '\n';
}
星期四 AcWing 3697. 回文子序列
注意:問的是回文子序列,不是子串。
長度大於等於3的回文子序列 等價於 兩個相等的元素位置之差大於1
所以:遍歷數組,找出兩個相等的元素。如果位置之差大於1就輸出 YES。
如果遍歷完數組,也沒找到,就輸出 NO。
當然也可以用哈希表記錄下元素出現的位置,在 \(O(N)\) 時間內過掉。這個方法可以看看其他題解。
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n);
for (int &x : a)cin >> x;
bool f = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n and !f; ++i)
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j)
if (a[i] == a[j] and j - i > 1) f = true;
cout << (f ? "YES\n" : "NO\n");
}
Week 7
星期一 AcWing 3705. 子集mex值
通過維護兩個變量從0開始,如果有0、1、2、3...這樣的直接慢慢向上疊加
const int N = 1e5 + 100;
ll n, a[N];
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)cin >> a[i];
sort(a, a + n);
ll m = 0, k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (a[i] == m)m++;
else if (a[i] == k)k++;
}
cout << m + k << endl;
}
星期二 AcWing 3711. 方格塗色
待補
const int N = 1e5+10;
int main(){
int t; scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--){
int n, u, r, d, l;
scanf("%d %d %d %d %d", &n, &u, &r, &d, &l);
int top, bottom, right ,left;
bool f = 0;
top = bottom = right = left = 0;
if(u == n) top = 2;
else if(u == n-1) top = 1;
if(r == n) right = 2;
else if(r == n-1) right = 1;
if(d == n) bottom = 2;
else if(d == n-1) bottom = 1;
if(l == n) left = 2;
else if(l == n-1) left = 1;
// printf("%d %d %d %d\n",top, bottom, right, left);
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++){
int a[4] = {0,0,0,0}, cnt = 0;
while(i>>cnt){
a[cnt] = (i>>cnt)&1;
cnt++;
}
if(a[0]+a[1] >= top && a[0]+a[1] <= u)
if(a[0]+a[2] >= left && a[0]+a[2] <= l)
if(a[1]+a[3] >= right && a[1]+a[3] <= r)
if(a[2]+a[3] >= bottom && a[2]+a[3] <= d)
f = 1;
}
if(f) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
}
}
星期三 AcWing 3720. 數組重排
因為對於每個 ai+bi 都要滿足 <=x 這個條件
我們只需要貪心的 使得每個和盡可能的小即可
所以對兩個數組 按升序 和 降序 sort 一下即可
void solve() {
int n, x;
cin >> n >> x;
vector<int> A(n, 0), B(n, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
cin >> A[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
cin >> B[i];
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
sort(B.begin(), B.end(), greater<int>());
bool ok = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (A[i] + B[i] > x)
ok = false;
cout << (ok ? "Yes" : "No") << endl;
}
星期四 AcWing 3725. 賣罐頭
math
ll _, n, x;
void solve() {
ll l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
ll a = r + 1;
if (l % a >= (a + 1) / 2) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
}
星期五 AcWing 3729. 改變數組元素
int arr[200001];
int res[200001];
void solve() {
int n, i, mn = 1e9;
cin >> n;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> arr[i];
for (i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
mn = min(mn, i - arr[i]);
res[i] = (mn < i);
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << res[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
Week 8
星期一 AcWing 3730. 尋找序列
由於題目保證 \(a_i \not= b_i \not = c_i\)所以直接逐位判斷選什么即可,時間復雜度 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i];
vector<int> b(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> b[i];
vector<int> c(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> c[i];
vector<int> p(n, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p[i] = a[i];
if (p[i] == p[(i + 1) % n] || p[i] == p[(i + n - 1) % n]) {
p[i] = b[i];
if (p[i] == p[(i + 1) % n] || p[i] == p[(i + n - 1) % n]) {
p[i] = c[i];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i > 0) cout << " ";
cout << p[i];
}
cout << '\n';
}
星期二 AcWing 3731. 序列湊零
ll _, n;
void solve() {
cin >> n;
int a[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2) cout << a[i + 1] << ' ' << -a[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
星期三 AcWing 3732. 矩陣復原
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 510, M = N * N;
int n, m, k;
int g[N][N];
PII pos[M];
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++ j) {
int x;
cin >> x;
pos[x].y = j;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j) {
int x;
cin >> x;
pos[x].x = j;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n * m; ++ i) {
auto &p = pos[i];
g[p.x][p.y] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++ j) {
cout << g[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr);
int _; for (cin >> _; _--;) solve();
return 0;
}
