這篇blog是我記錄自己開始做科研的一些筆記、參考了一些論文和各種博客和一些自己的思考和想法。由於網上相關圖像質量評估的整理資料相對較少,如果能幫到看到這篇文章的你,那真是非常棒!會持續更新補全一些東西,請強迫症的朋友見諒一些沒有內容的目錄~
如有侵權和錯誤,請聯系我進行刪改~
一. 概述
圖像質量是比較各種圖像處理算法性能優劣以及優化系統參數的重要指標,因此在圖像采集、編碼壓縮、網絡傳輸等領域建立有效的圖像質量評價機制具有重要的意義。
圖像質量評價就是對圖像進行評分,有人對圖像質量評價的方法,也有通過計算機來進行對圖像質量的評估的方法。
主觀評價方法就是通過人來進行類似心理學或者社會學領域的對圖像的評分實驗,來進行基於個體的主觀對圖像的評價,這種方法顯示需要通過一個比較固定的步驟。1、准備數據集;2、邀請觀察者進行圖像評分;3、對評分結果進行處理得出圖像質量評價最終得分。
客觀評價方法就是通過計算機的根據數字圖像處理的基本原理來進行對圖像質量評價設計算法,並評價算法好壞,最終得出最有效的圖像質量評價算法應用到后續對圖像質量評價的工作中。
二. 主觀評價方法
主觀質量評價分為絕對主觀評價和相對主觀評價方法兩類,絕對主觀評價是在無標准的參考情況下,將圖像直接按照視覺感受分級評分。相對主觀評價方法即在有標准圖像的情況下,由觀察者將一批圖像從好到壞進行分類,將它們相互比較得出好壞,並給出相應的評分。

2.1 雙刺激損傷分級法
給原始圖像、失真圖像對比觀察受損情況,選出失真圖像的評分。
2.2 雙刺激連續質量分級法
給兩組圖像,不提前告知失真與不失真,分別對全部圖像進行評分,計算DMOS。
DMOS越小,說明待測圖像的質量越好。
2.3 單刺激連續質量分級法
只觀察失真圖像,選出評分。
2.4 MOS與DMOS
觀測者進行評價時 ,其情緒 、動機 、知識背景等因素均會對評價結果產生影響 ,使評價結果變得不准確。
平均主觀得分 (Mean opinion score, MOS)
平均主觀得分差異 (Differential mean opinion score, DMOS)
在下面的描述中,$i=1, ..., M $代表不同的觀測者 \(j= 1, ..., N\) 代表不同的圖像 ,r代表觀測者對一幅圖像的原始評分。
a) 評分出界的檢測。對於同一測試組中同一幅圖像的主觀評價值,其均值、標准差為 :
其中 \(r_{i, j}\) 為一個主觀評分, \([U-\varepsilon, U+\varepsilon]\) 為 \(95 \%\) 置信區間,在 比區間之外的評分被視為出界評分,舍棄。評分出界檢測做 \(1\sim 2\) 次。
b) 對觀測者的淘汰。如果同一測試組內某一個觀測者 勻評分出界次數 \(N \geqslant N_{0}\), 則認為該觀測者不具備評價的資 各,舍棄他的全部評價值。其中 \(N_{0}\) 為經驗值,參考值為 16 。
采用“雙刺激法”,即同時給出失真圖像和參考圖像,要求觀測者對二者都進行評分,以評分之差作為評價結果。
某中 \(r_{i, ref(j)}\) 是第 \(i\) 個觀測者對第 \(j\) 幅圖像的參考圖像的評分, \({d}^{\prime}{ }_{i, j}\) 是對每一個觀測者的評分進行歸一化后的結果。 最后,得到一幅圖像的 DMOS值;
三. 客觀評價方法
全參考是需要參考圖像的全部信息進行像素值級別的一一對應比較評分,這類方法准確性好,但是參考圖像難以獲得;半參考需要參考圖像的部分統計特征來進行比較評分,在實際的應用中具有傳輸數據量小的優勢;全參考是無需參考圖像直接通過算法對圖像進行質量評價,在應用上比較靈活。
3.1 全參考(Full Reference)
-
均方差 MSE
\[\operatorname{MSE}=\frac{\sum_{m=1}^{M} \sum_{n=1}^{N}[R(m, n)-I(m, n)]^{2}}{M \times N} \]式中,R( m,n) 代表參考圖像在空間位置( m,n) 的灰度值,I( m,n) 代表失真圖像在空間位置的( m,n) 的灰度值;
-
峰值信噪比 PSNR
\[\mathrm{PSNR}=10 \ln \frac{L^{2}}{\mathrm{MSE}} \]L 為峰值信號,對於 8 位的灰度圖像來說,L = 255;
-
- Bo W , Wang Z , Liao Y , et al. HVS-based structural similarity for image quality assessment. International Conference on Signal Processing.
-
多尺度結構相似度 MSSIM
-
基於梯度的結構相似度 GSSIM
-
信息保真度准則 IFC
-
視覺信息保真度 VIF
-
特征相似性 FSIM
- Zhang L , Zhang L , Mou X , et al. FSIM: A Feature Similarity Index for Image Quality Assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(8):2378-2386.
- Feature Similarity Index for Image Quality Assessment
-
GMSD
-
- Y. Lv, G. Jiang, M. Yu, H. Xu, F. Shao, and S. Liu. Difference of Gaussian statistical features based blind image quality as sessment: A deep learning approach. In IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pages 2344–2348, 2015.
-
FR-DCNN
-
- Kim J , Lee S . Deep Learning of Human Visual Sensitivity in Image Quality Assessment Framework[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2017:1969-1977.
- Deep Image Quality Assessment 深度圖像質量評價
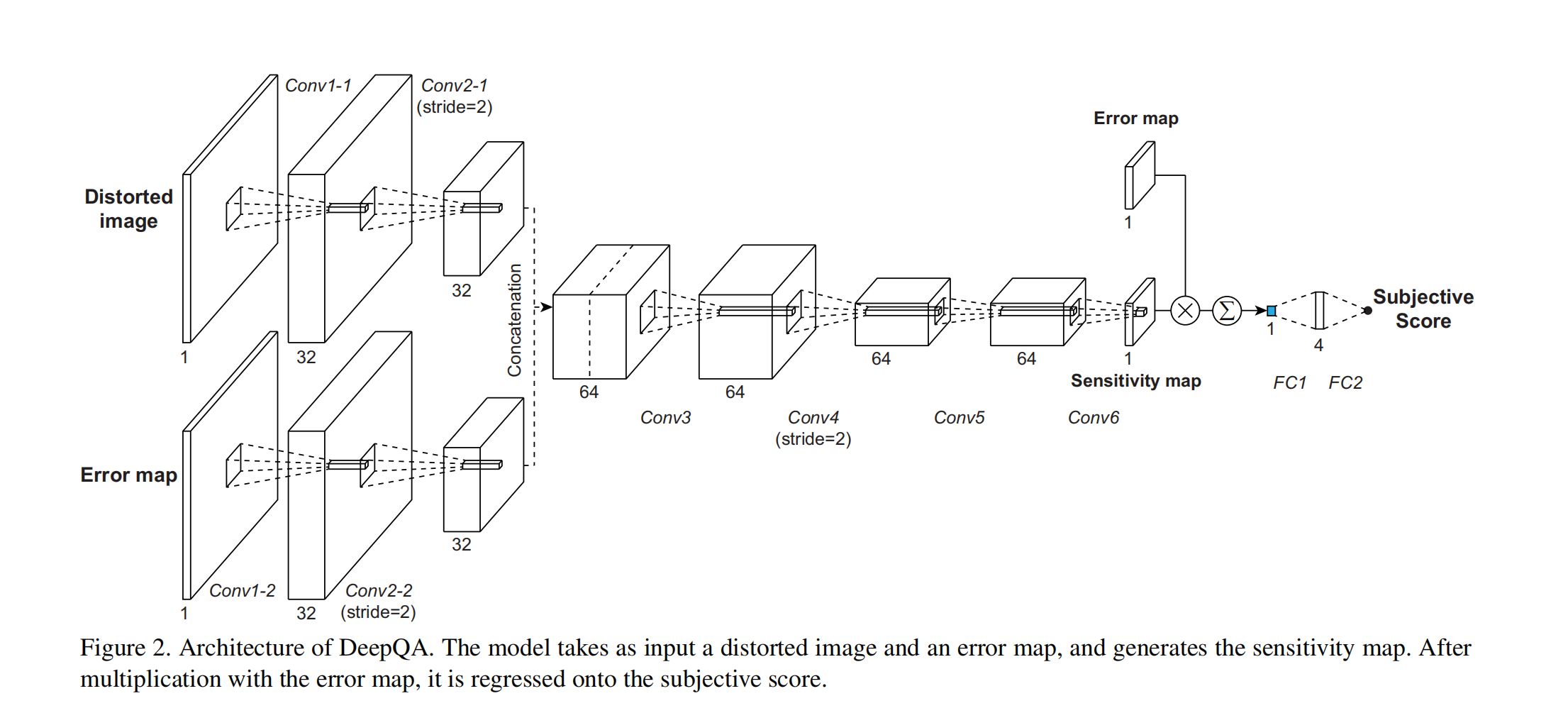
-
-
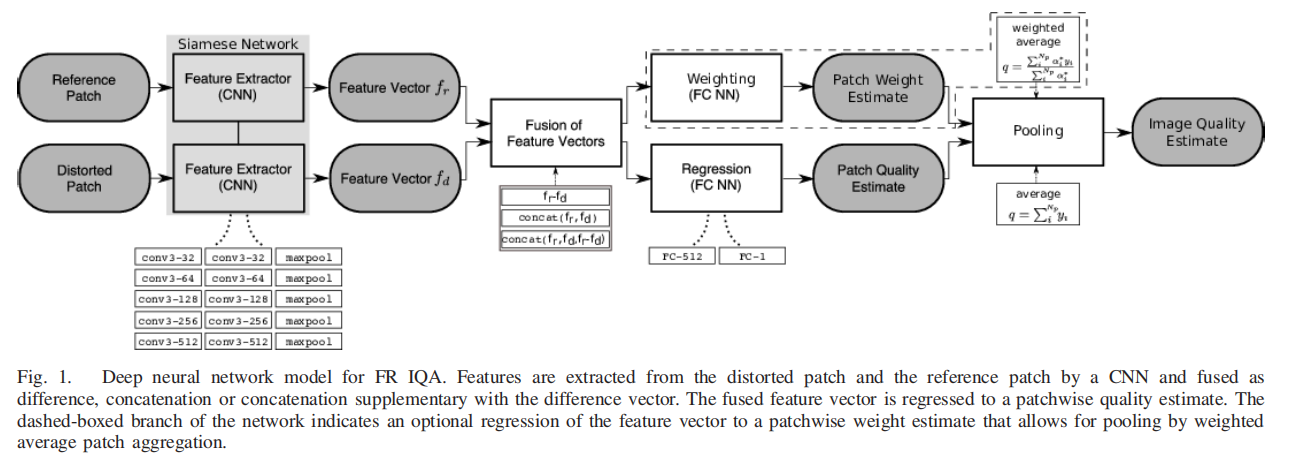
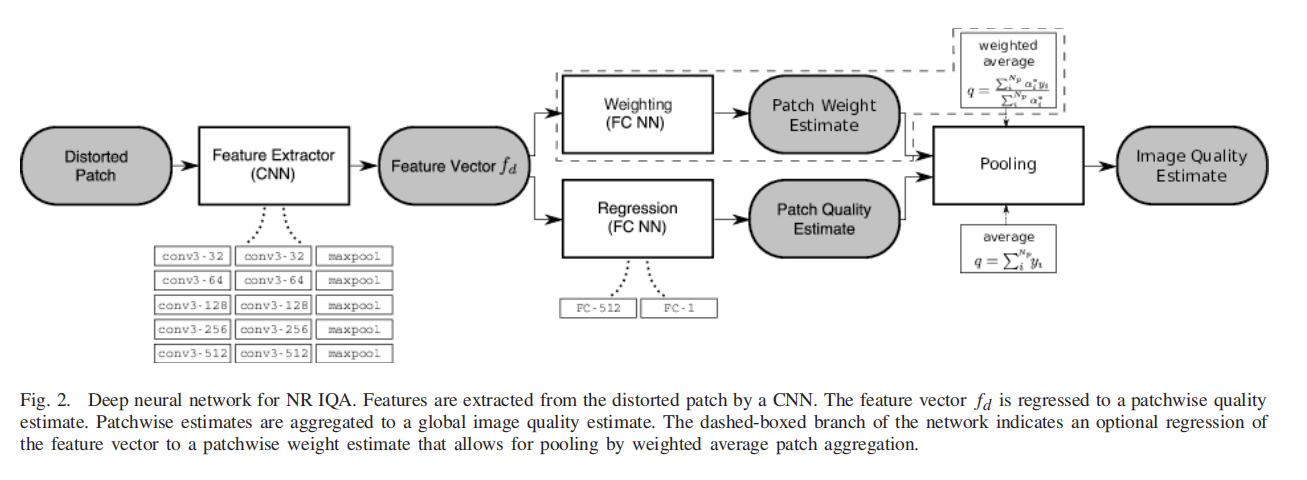
Bosse S , Maniry D , Muller K R , et al. Deep Neural Networks for No-Reference and Full-Reference Image Quality Assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017:1-1.
-
Weighted Average Deep Image QuAlity Measure for FR IQA (WaDIQaM-FR).
-
-
3.2 半參考(Reduced Reference)
- MGA
- FSI
3.3 無參考(No Reference\Bind IQA)
-
- A. Mittal, A. K. Moorthy, and A. C. Bovik, “No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 21, no. 12, pp. 4695–4708, Dec. 2012.
- blind/referenceless image spatial quality evaluator 盲/無參考圖像空間質量評價器
- 傳統方法
-
- Jiang Q , F Shao, Lin W , et al. Optimizing Multistage Discriminative Dictionaries for Blind Image Quality Assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017.
- Optimizing Multistage Discriminative Dictionaries for Blind Image Quality Assessment
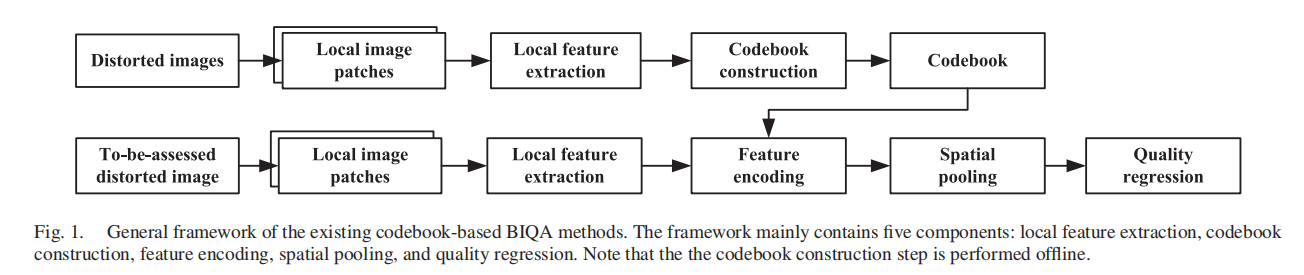
- 傳統方法
-
CNN
- L. Kang, P. Ye, Y. Li, and D. Doermann, “Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., Jun. 2014, pp. 1733–1740.
- 卷積神經網絡
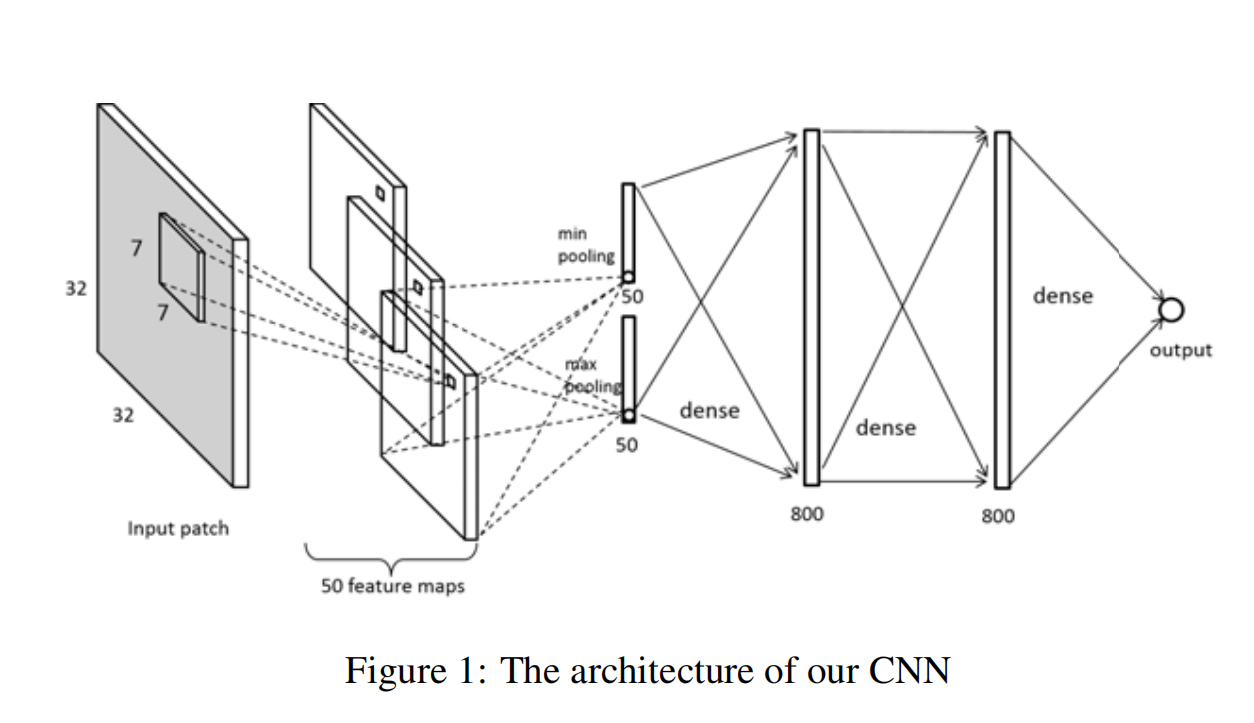
-
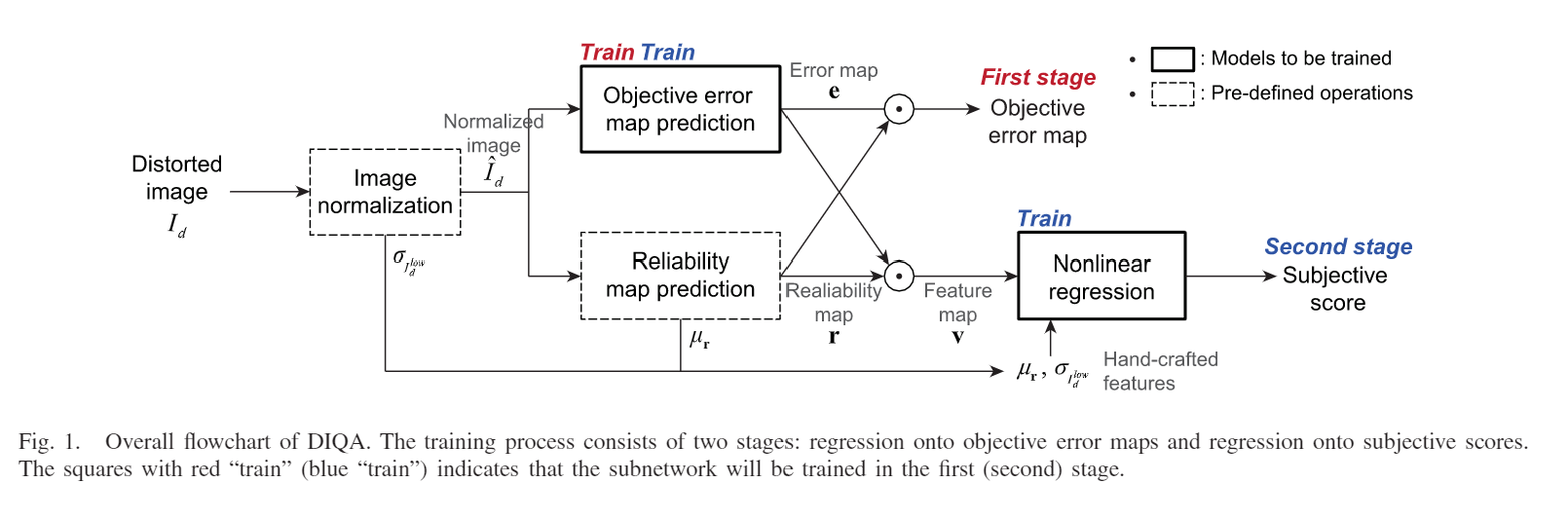
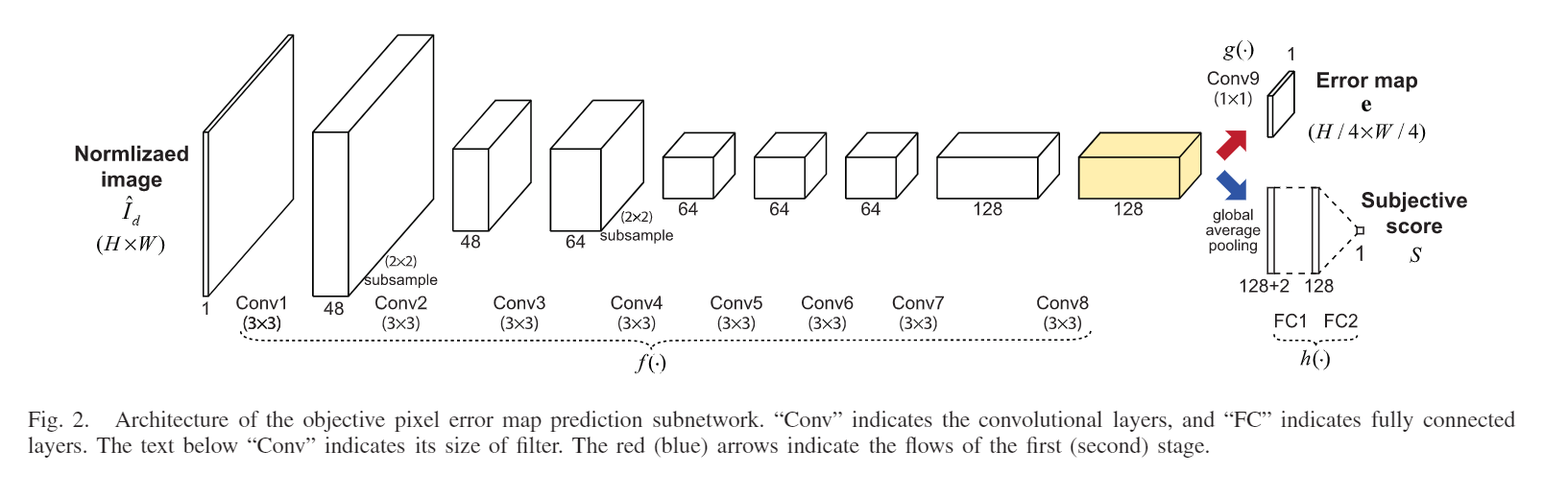
DIQA
-
Jongyoo K , Anh-Duc N , Sanghoon L . Deep CNN-Based Blind Image Quality Predictor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks & Learning Systems, 2018, PP:1-14.
-
-
-
- F. Gao, J. Yu, S. Zhu, Q. Huang, and Q. Tian, ‘‘Blind image quality prediction by exploiting multi-level deep representations,’’ Pattern Recognit., vol. 81, pp. 432–442, Sep. 2018.
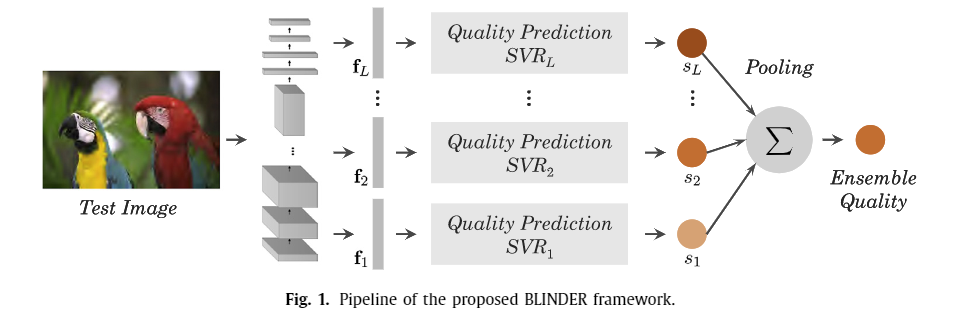
-
- X. Liu, J. van de Weijer, and A. D. Bagdanov, ‘‘RankIQA: Learning from rankings for no-reference image quality assessment,’’ in Proc. IEEE Conf. ICCV, Jun. 2017, pp. 1040–1049.
- a no-reference image quality assessment(NR-IQA) approach that learns from rankings (RankIQA).
- 代碼:https://github.com/xialeiliu/RankIQA
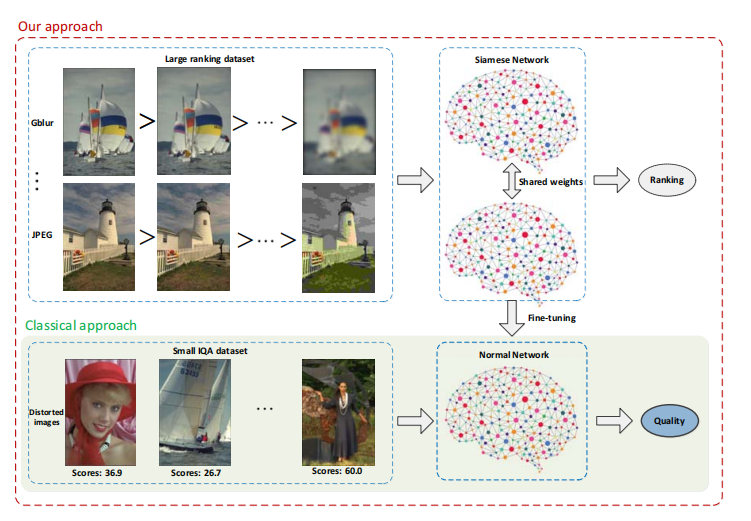
-
- K. Ma, W. Liu, K. Zhang, Z. Duanmu, Z. Wang, and W. Zuo, “End-to-end blind image quality assessment using deep neural networks,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 1202–1213, Mar. 2018.
- multi-task end-to-end optimized deep neural network 多任務端到端優化深度神經網絡
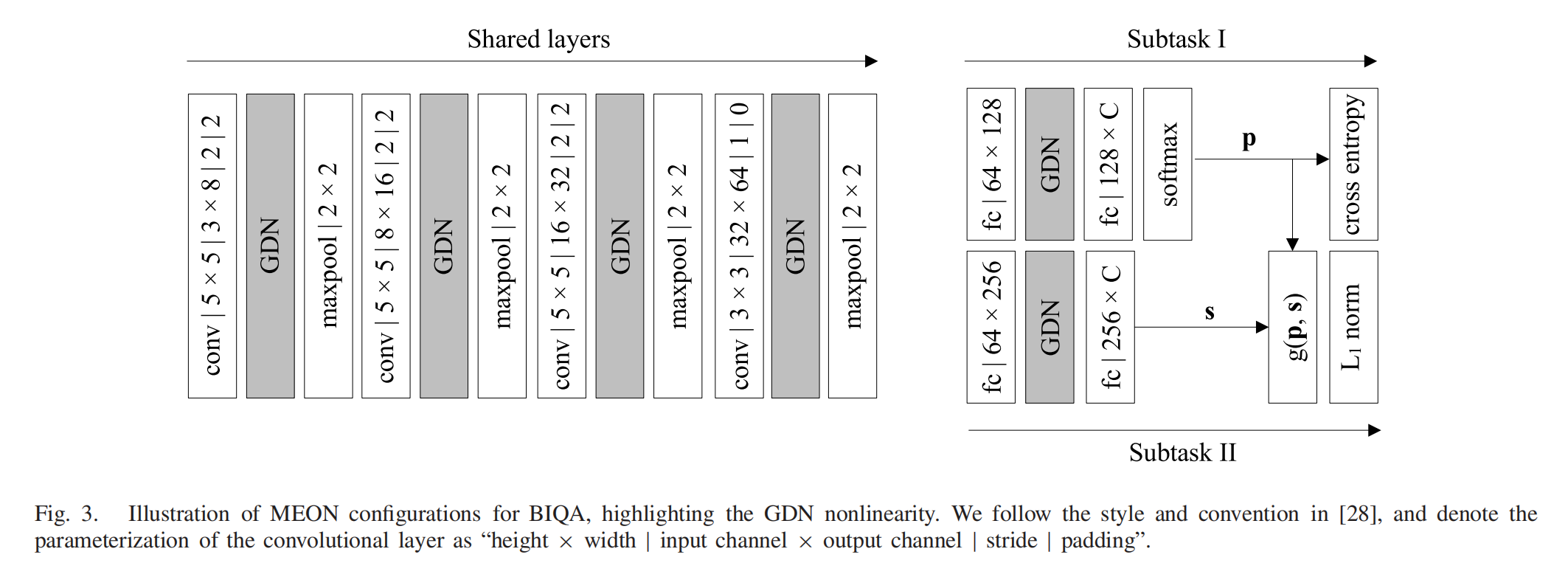
-
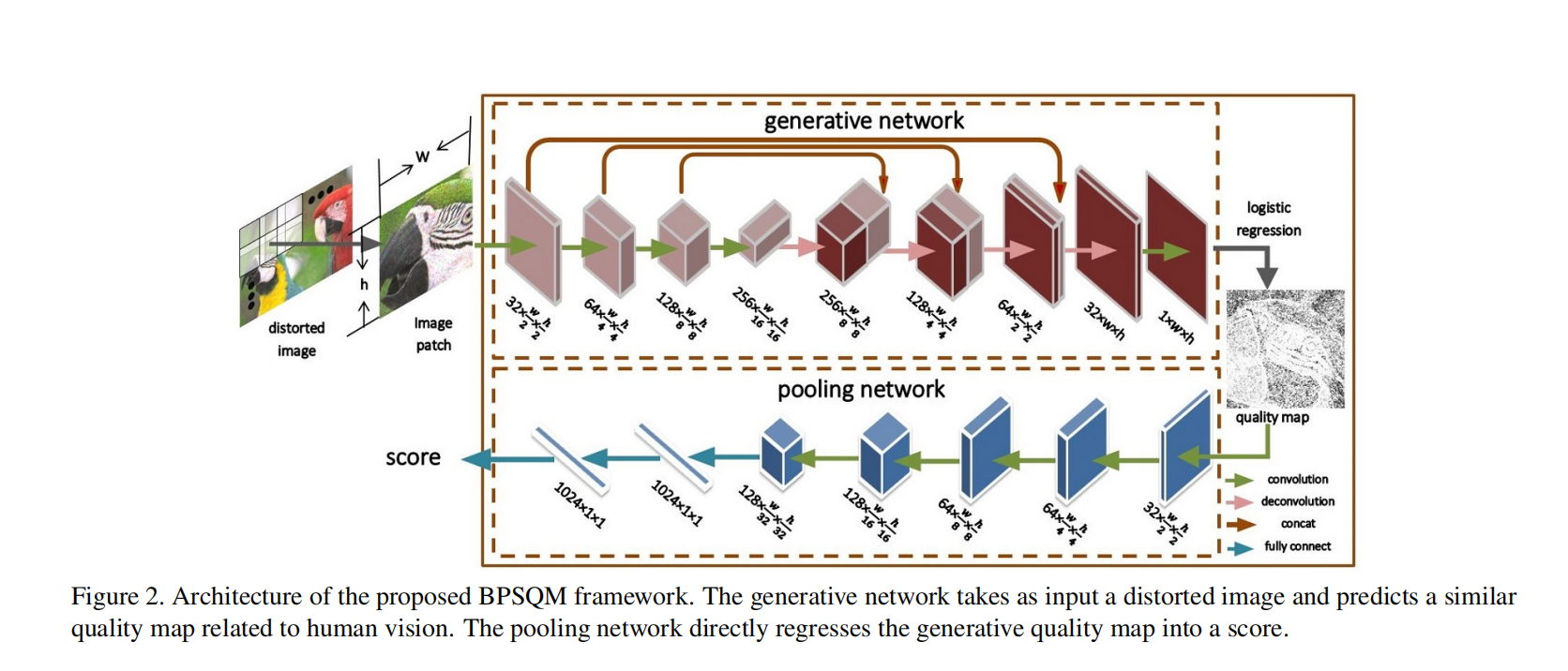
BPSQM
-
D. Pan, P. Shi, M. Hou, Z. Ying, S. Fu, and Y. Zhang, ‘‘Blind predicting similar quality map for image quality assessment,’’ in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), Jun. 2018, pp. 6373–6382.
-
Blind predicting similar quality map for image quality assessment
盲預測相似質量圖
-
-
-
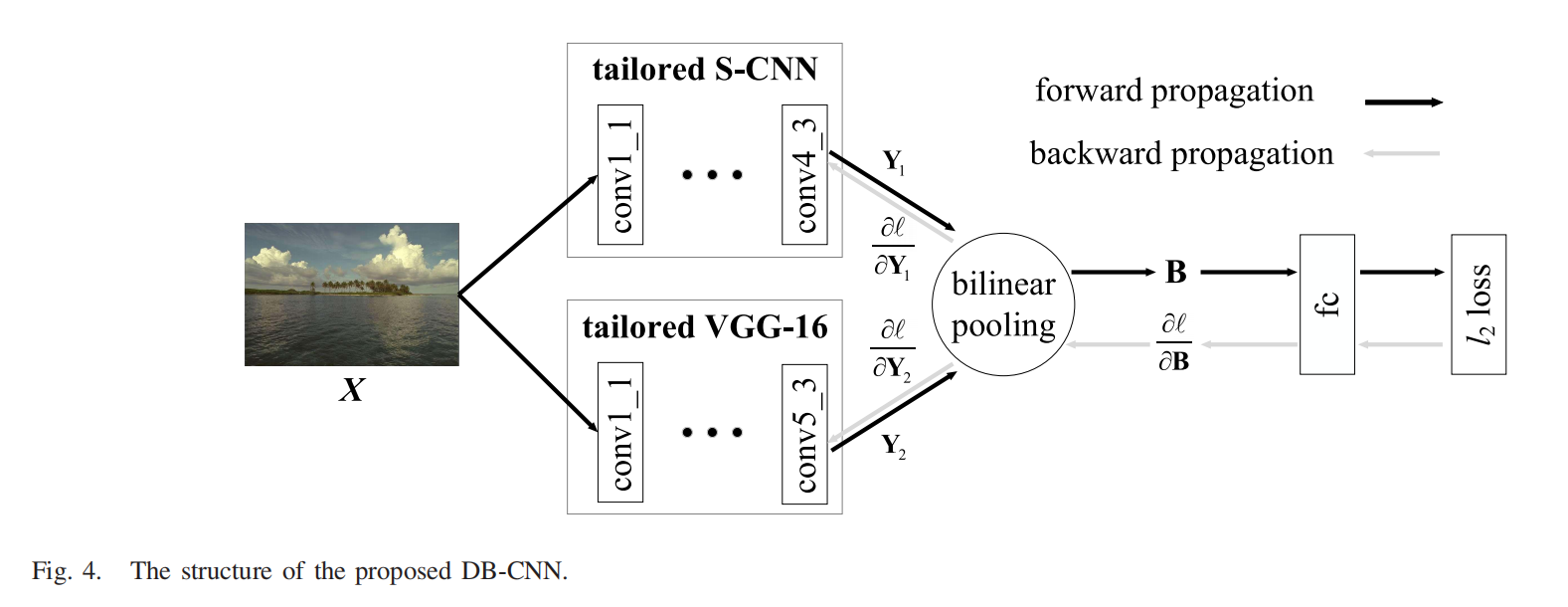
- Zhang W , Ma K , Yan J , et al. Blind Image Quality Assessment Using A Deep Bilinear Convolutional Neural Network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems for Video Technology, 2019:1-1.
- deep bilinear CNN (DB-CNN) 深度雙線性CNN
- 代碼:https://github.com/zwx8981/DBCNN-PyTorch
-
- Zhou W , Chen Z , Li W . Dual-Stream Interactive Networks for No-Reference Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019:1-1.
- stereoscopic image quality assessment (SIQA) 立體圖像質量評價

-
-
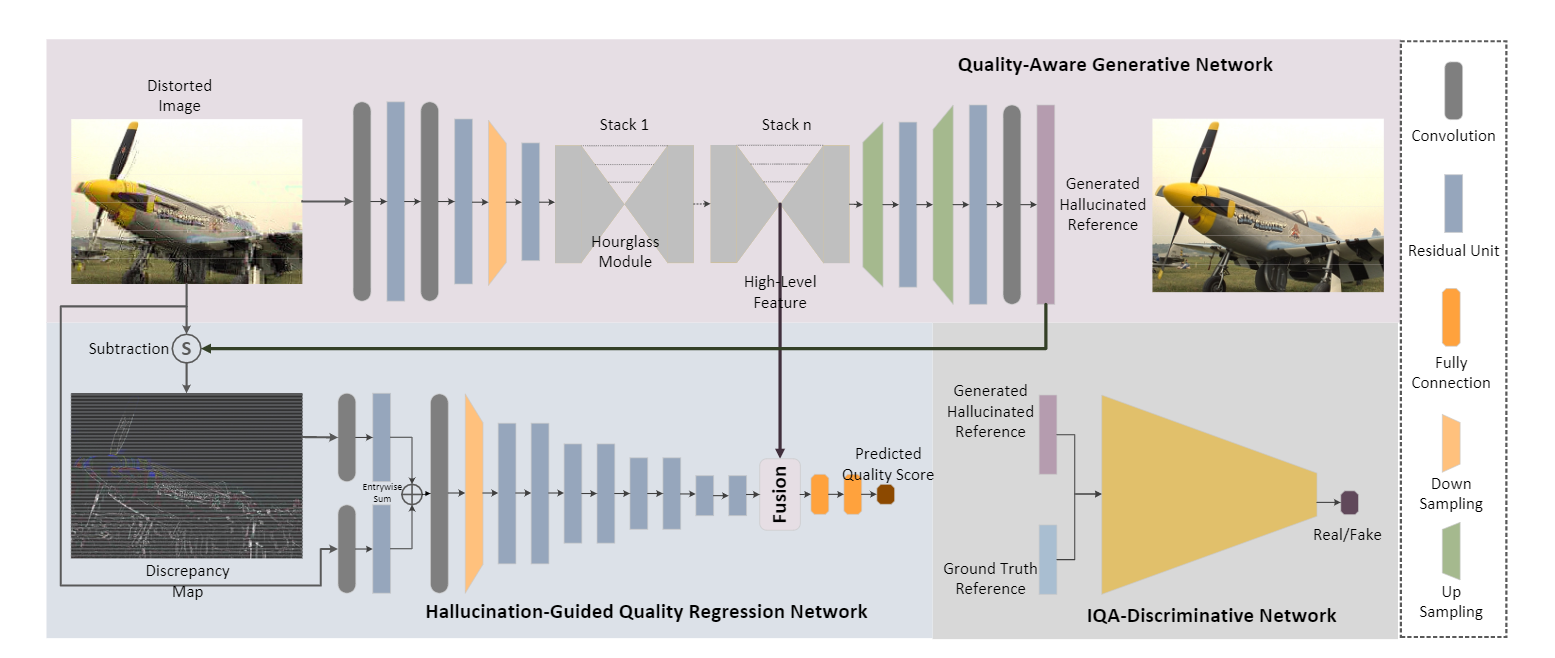
Lin K Y , Wang G . Hallucinated-IQA: No-Reference Image Quality Assessment via Adversarial Learning[C]// 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 2018.
-
Hallucinated-IQA: No-reference image quality assessment via adversarial learning
-
-
GAN
-
四. 數據集
百度雲
鏈接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1AgB0IO2IGLBZ_nhzhMZd9g
提取碼:vuhb
復制這段內容后打開百度網盤手機App,操作更方便哦)
- live
- TID
4.1 LIVE
內容:29幅參考圖像,779幅失真圖像
圖像大小:尺寸大小不一(.bmp)
5種失真類型:JPEG2000(175幅),JPEG(169幅),白噪聲(145幅),高斯模糊(145幅),快速瑞利衰減(145幅)
標簽:DMOS取值范圍[0,100],161個觀察者
LIVE含有兩個圖像質量評估的數據集:
LIVE Image Quality Assessment Database
29張圖片,5種失真類型:
| 失真類型 | 英文 | 文件夾 | 圖片數 | info |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG2000 | JPEG2000 | jp2k | 227 | 比特率 |
| JPEG | JPEG | jpeg | 233 | 比特率 |
| 白化噪聲 | White Noise | wn | 174 | 標准差 sigma |
| 高斯模糊 | Gaussian Blur | gblur | 174 | 標准差 sigma |
| 快速衰落瑞利(誤碼) | Fast Fading Rayleigh | fastfading | 174 | 失真強度 |
| 原圖 | - | refimgs | 29 | - |
LIVE Multiply Distorted Image Quality Database
4.2 TID 2008
內容:25幅參考圖像,1700幅失真圖像
圖像大小:512x384(.bmp)
17種失真類型:加性高斯噪聲、顏色分量強於照明分量的加性噪聲、空間位置相關噪聲、掩膜噪聲、高頻噪聲、脈沖噪聲、量化噪聲、高斯模糊、圖像噪聲、JPEG壓縮、JPEG2000壓縮、JPEG傳輸錯誤、JPEG2000傳輸錯誤、非偏心式噪聲、不同強度的局部塊失真、強度均值偏移以及對比度變化,4種失真水平。
標簽:MOS取值范圍為[0,9],838個觀察者
4.3 TID 2013
內容:25幅參考圖像,3000幅失真圖像
圖像大小:512x384(.bmp)
24種失真類型:比TID2008增加七種:改變色彩飽和度、多重高斯噪聲、舒適噪聲、有損壓縮、彩色圖像量化、色差以及稀疏采樣。5失真水平
標簽:MOS取值范圍為[0,9],971個觀察者
失真類型(Types of distortion):
| 編號 | 失真類型 | 英文 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 高斯噪聲 | Additive Gaussian noise |
| 2 | 在顏色分量中添加噪聲,在亮度分量中添加噪聲,且顏色強於亮度 | Additive noise in color components is more intensive than additive noise in the luminance component |
| 3 | 空間相關噪聲 | Spatially correlated noise |
| 4 | 掩碼噪聲 | Masked noise |
| 5 | 高頻噪聲 | High frequency noise |
| 6 | 脈沖噪聲 | Impulse noise |
| 7 | 量化噪聲 | Quantization noise |
| 8 | 高斯模糊 | Gaussian blur |
| 9 | 圖像去噪 | Image denoising |
| 10 | JPEG壓縮 | JPEG compression |
| 11 | JPEG2000壓縮 | JPEG2000 compression |
| 12 | JPEG2000壓縮 | JPEG2000 transmission errors |
| 13 | JPEG傳輸錯誤 | JPEG transmission errors |
| 14 | 非偏心模式噪聲 | Non eccentricity pattern noise |
| 15 | 不同強度的局部塊狀扭曲 | Local block-wise distortions of different intensity |
| 16 | 平均移位(強度移位) | Mean shift (intensity shift) |
| 17 | 對比度變化 | Contrast change |
| 18 | 顏色飽和度的變化 | Change of color saturation |
| 19 | 乘法高斯噪聲 | Multiplicative Gaussian noise |
| 20 | 舒適的噪聲 | Comfort noise |
| 21 | 噪聲圖像的有損壓縮 | Lossy compression of noisy images |
| 22 | 抖動的圖像顏色量化 | Image color quantization with dither |
| 23 | 色差 | Chromatic aberrations |
| 24 | 稀疏采樣和重建 | Sparse sampling and reconstruction |
4.4 CSIQ
內容:30幅參考圖像,866幅失真圖像,
圖像大小:512x512 (.png)
6種失真類型:JPEG壓縮、JPEG2000壓縮、整體對比度縮減、加性高斯粉紅噪聲、加性高斯白噪聲以及高斯模糊,5種失真等級
標簽:DMOS取值范圍為[0,1],25個觀察者
4.5 IVC
內容:10幅參考圖像,235幅失真圖像
圖像大小:
4種失真類型:JPEG壓縮、JPEG2000壓縮、LAR編碼和模糊
標簽: 由 15 位測試人員, 庫中的 MOS 值取值范圍為 [1, 5],
4.6 SIQAD
4.7 CID2013
4.8 LIVE-itW
4.9 KonIQ-10K
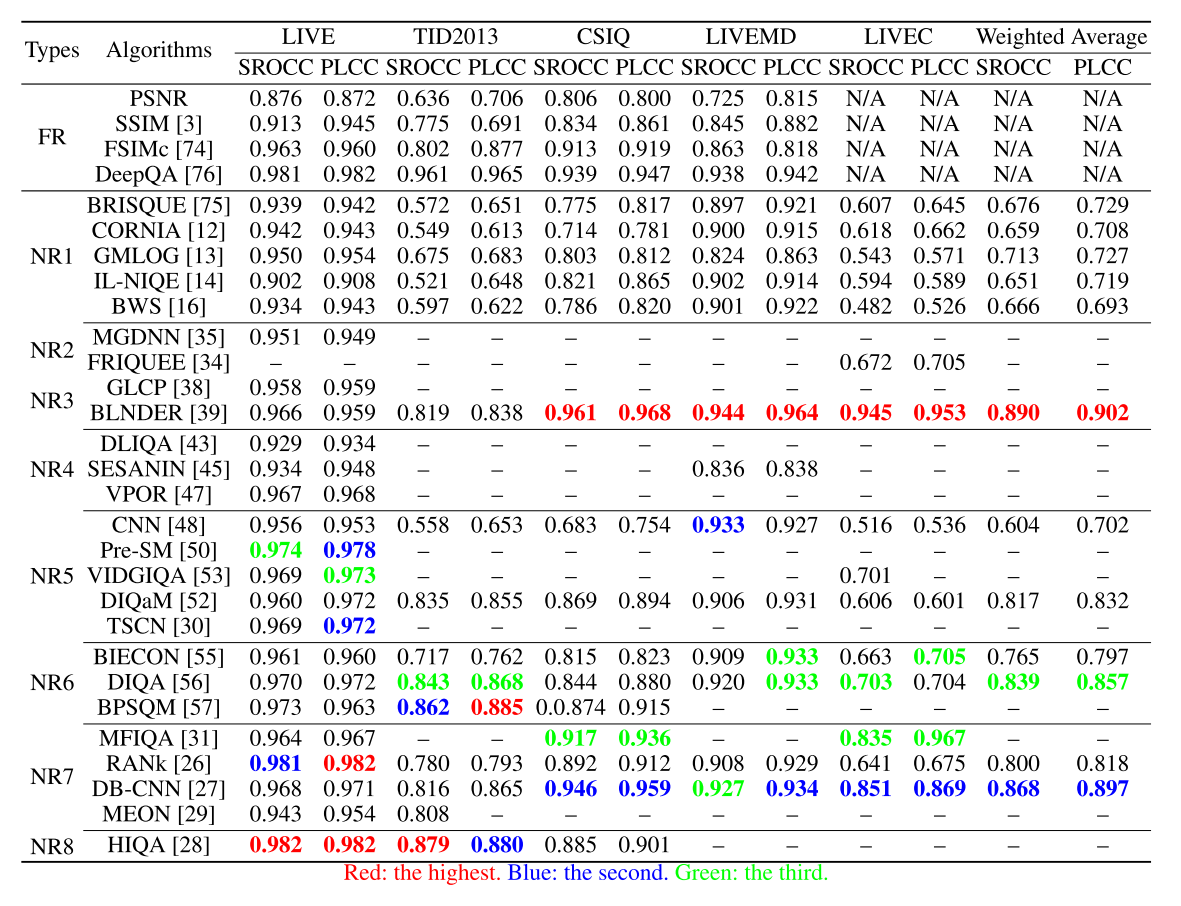
五. 算法性能衡量指標
5.1 SROCC
Spearman Rank Order Correlation Coefficient
Spearman秩相關系數
其中, \(r_{xi}\), \(r_{yi}\) 分別為 \(x_i\) 和 \(y_i\) 在各自數據序列中的排序位置. Spearman 秩線性相關系數衡量算法預測的單調性 (Monotonicity).
5.2 LCC
Linear Correlation Coefficient
線性相關系數
其中, \(\bar{x}, \bar{y}\) 分別為 \(\left\{x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{n}\right\}\) 和 \(\left\{y_{1}, y_{2},...y_{n}\right\}\) 的均值, \(\sigma_{x},\sigma_{y}\)分別為它們]的標准差。線性相關系數描 述算法評價值與人眼主觀打分之間的相關性, 也衡量了算法預測的准確性。
5.3 RMSE
Root Mean Square Error
均方根誤差
其中, \(\left\{x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{n}\right\}\) 表示人眼打分的 MOS 或 \(\mathrm{DMOS}\) 值, \(\left\{y_{1}, y_{2}, \cdots, y_{n}\right\}\) 表示某種算法估計圖像質量值. 均方根誤差比較算法評價值與人眼主觀打 分之間的絕對誤差, 衡量算法預測的准確性 (Accuracy)。
六、失真類型及算法實現
- JPEG2000失真
- JPEG失真
- 白噪聲失真
- 高斯模糊失真
- 快速瑞利衰減失真
- 整體對比度縮減
- 加性高斯粉紅噪聲
- 加性高斯白噪聲
- 高斯模糊
- 顏色分量強於照明分量的加性噪聲
- 空間位置相關噪聲
- 掩膜噪聲
- 高頻噪聲
- 脈沖噪聲
- 量化噪聲
- 圖像噪聲
- 不同強度的局部塊失真
- 強度均值偏移
- 多重高斯噪聲
6.1 Matlab
J = imnoise(I,'gaussian') %將方差為 0.01 的零均值高斯白噪聲添加到灰度圖像 I。
J = imnoise(I,'gaussian',m) %添加高斯白噪聲,均值為 m,方差為 0.01。
J = imnoise(I,'gaussian',m,var_gauss) %添加高斯白噪聲,均值為 m,方差為 var_gauss
J = imnoise(I,'localvar',var_local) %添加局部方差為 var_local 的零均值高斯白噪聲。
J = imnoise(I,'localvar',intensity_map,var_local) %添加零均值高斯白噪聲。噪聲的局部方差 var_local 是 I 中圖像強度值的函數。圖像強度值到噪聲方差的映射由向量 intensity_map 指定。
J = imnoise(I,'poisson') %從數據中生成泊松噪聲,而不是向數據中添加人為噪聲。
J = imnoise(I,'salt & pepper') %添加椒鹽噪聲,默認噪聲密度為 0.05。這會影響大約 5% 的像素。
J = imnoise(I,'salt & pepper',d) %添加椒鹽噪聲,其中 d 是噪聲密度。這會影響大約 d*numel(I) 個像素。
J = imnoise(I,'speckle') %使用方程 J = I+n*I 添加乘性噪聲,其中 n 是均值為 0、方差為 0.05 的均勻分布隨機噪聲。
J = imnoise(I,'speckle',var_speckle) % 添加方差為 var_speckle 的乘性噪聲。
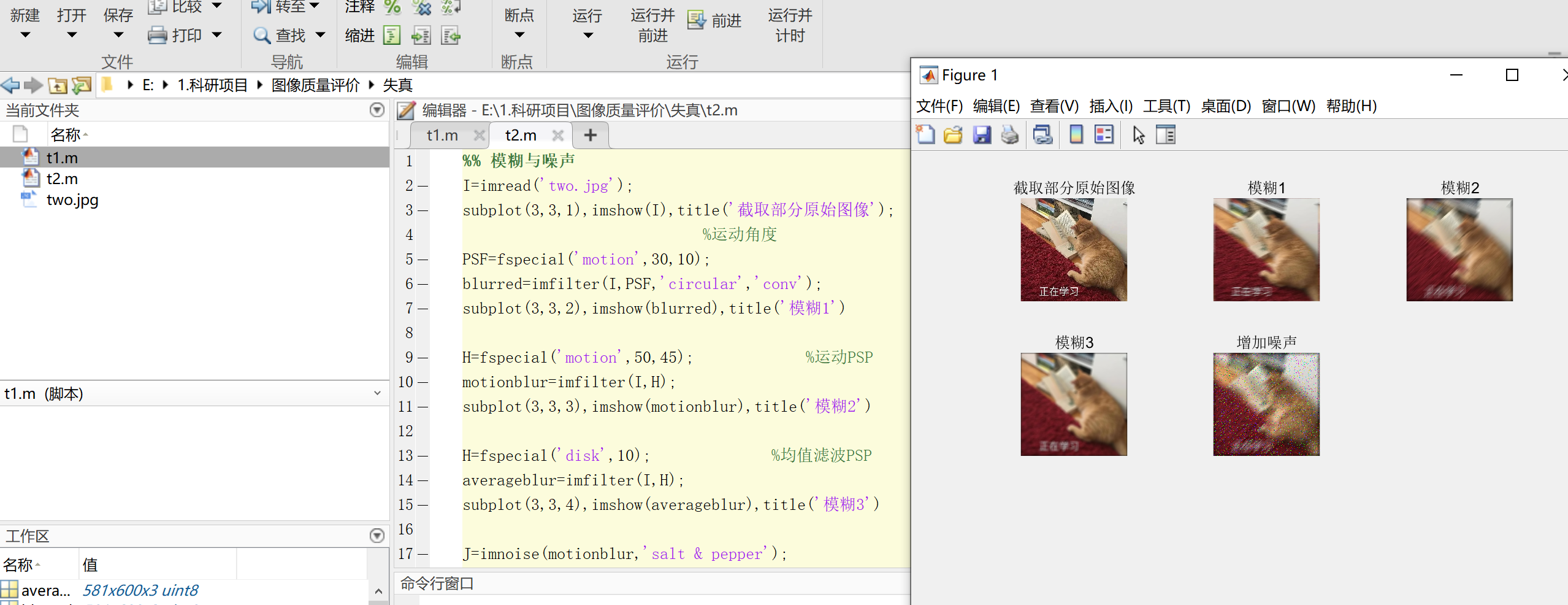
%% 模糊與噪聲
I=imread('two.jpg');
subplot(3,3,1),imshow(I),title('截取部分原始圖像');
%運動角度
PSF=fspecial('motion',30,10);
blurred=imfilter(I,PSF,'circular','conv');
subplot(3,3,2),imshow(blurred),title('模糊1')
H=fspecial('motion',50,45); %運動PSP
motionblur=imfilter(I,H);
subplot(3,3,3),imshow(motionblur),title('模糊2')
H=fspecial('disk',10); %均值濾波PSP
averageblur=imfilter(I,H);
subplot(3,3,4),imshow(averageblur),title('模糊3')
J=imnoise(motionblur,'salt & pepper');
subplot(3,3,5),imshow(J),title('增加噪聲');
6.2 python 運動模糊
import numpy as np
import cv2
def motion_blur(image, degree=12, angle=45):
image = np.array(image)
# 這里生成任意角度的運動模糊kernel的矩陣, degree越大,模糊程度越高
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((degree / 2, degree / 2), angle, 1)
motion_blur_kernel = np.diag(np.ones(degree))
motion_blur_kernel = cv2.warpAffine(motion_blur_kernel, M, (degree, degree))
motion_blur_kernel = motion_blur_kernel / degree
blurred = cv2.filter2D(image, -1, motion_blur_kernel)
# convert to uint8
cv2.normalize(blurred, blurred, 0, 255, cv2.NORM_MINMAX)
blurred = np.array(blurred, dtype=np.uint8)
return blurred
img = cv2.imread('./two.jpg')
img_ = motion_blur(img)
cv2.imshow('Source image', img)
cv2.imshow('blur image', img_)
cv2.waitKey()
6.3 python 高斯模糊
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('./two.jpg')
img_ = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, ksize=(9, 9), sigmaX=0, sigmaY=0)
cv2.imshow('Source image', img)
cv2.imshow('blur image', img_)
cv2.waitKey()
七、花粉圖像質量評價的思考
花粉圖像質量評價工作:
- 擴充數據集
- 手動(失真類型)
- 自動(GAN生成)
- 使用深度學習方法進行圖片質量評估
- DB-CNN
- HIQA
- 自動篩選有效圖像進行后續的基於良好的花粉圖像數據集的花粉識別與計數
