這篇主要記錄一下如何實現對數據庫的並行運算來節省代碼運行時間。語言是Python,其他語言思路一樣。
前言
一共23w條數據,是之前通過自然語言分析處理過的數據,附一張截圖:

要實現對news主體的讀取,並且找到其中含有的股票名稱,只要發現,就將這支股票和對應的日期、score寫入數據庫。
顯然,幾十萬條數據要是一條條讀寫,然后在本機上操作,耗時太久,可行性極低。所以,如何有效並行的讀取內容,並且進行操作,最后再寫入數據庫呢?
並行讀取和寫入
- 並行讀取:創建N*max_process個進程,對數據庫進行讀取。讀取的時候應該注意:
- 每個進程需要分配不同的connection和對應的cursor,否則數據庫會報錯。
- 數據庫必須能承受相應的高並發訪問(可以手動更改)
實現的時候,如果不在進程里面創建新的connection,就會發生沖突,每個進程拿到權限后,會被下個進程釋放,所以匯報出來NoneType Error的錯誤。
- 並行寫入:在對數據庫進行更改的時候,不可以多進程更改。所以,我們需要根據已有的表,創建max_process-1個同樣結構的表用來寫入。表的命名規則可以直接在原來基礎上加上1,2,3...數字可以通過對max_process取余得到。
此時,對應進程里面先后出現讀入的conn(保存消息后關閉)和寫入的conn。每個進程對應的表的index就是 主循環中的num對max_process取余(100->4,101->5),這樣每個進程只對一個表進行操作了。
部分代碼實現
max_process = 16 #最大進程數
def read_SQL_write(r_host,r_port,r_user,r_passwd,r_db,r_charset,w_host,w_port,w_user,w_passwd,w_db,w_charset,cmd,index=None):
#得到tem字典保存着信息
try:
conn = pymysql.Connect(host=r_host, port=r_port, user=r_user, passwd =r_passwd, db =r_db, charset =r_charset)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(cmd)
except Exception as e:
error = "[-][-]%d fail to connect SQL for reading" % index
log_error('error.log',error)
return
else:
tem = cursor.fetchone()
print('[+][+]%d succeed to connect SQL for reading' % index)
finally:
cursor.close()
conn.close()
try:
conn = pymysql.Connect(host=w_host, port=w_port, user=w_user, passwd =w_passwd, db =w_db, charset =w_charset)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(cmd)
except Exception as e:
error = "[-][-]%d fail to connect SQL for writing" % index
log_error('error.log',error)
return
else:
print('[+][+]%d succeed to connect SQL for writing' % index)
r_dict = dict()
r_dict['id'] = tem[0]
r_dict['content_id'] = tem[1]
r_dict['pub_date'] = tem[2]
r_dict['title'] = cht_to_chs(tem[3])
r_dict['title_score'] =tem[4]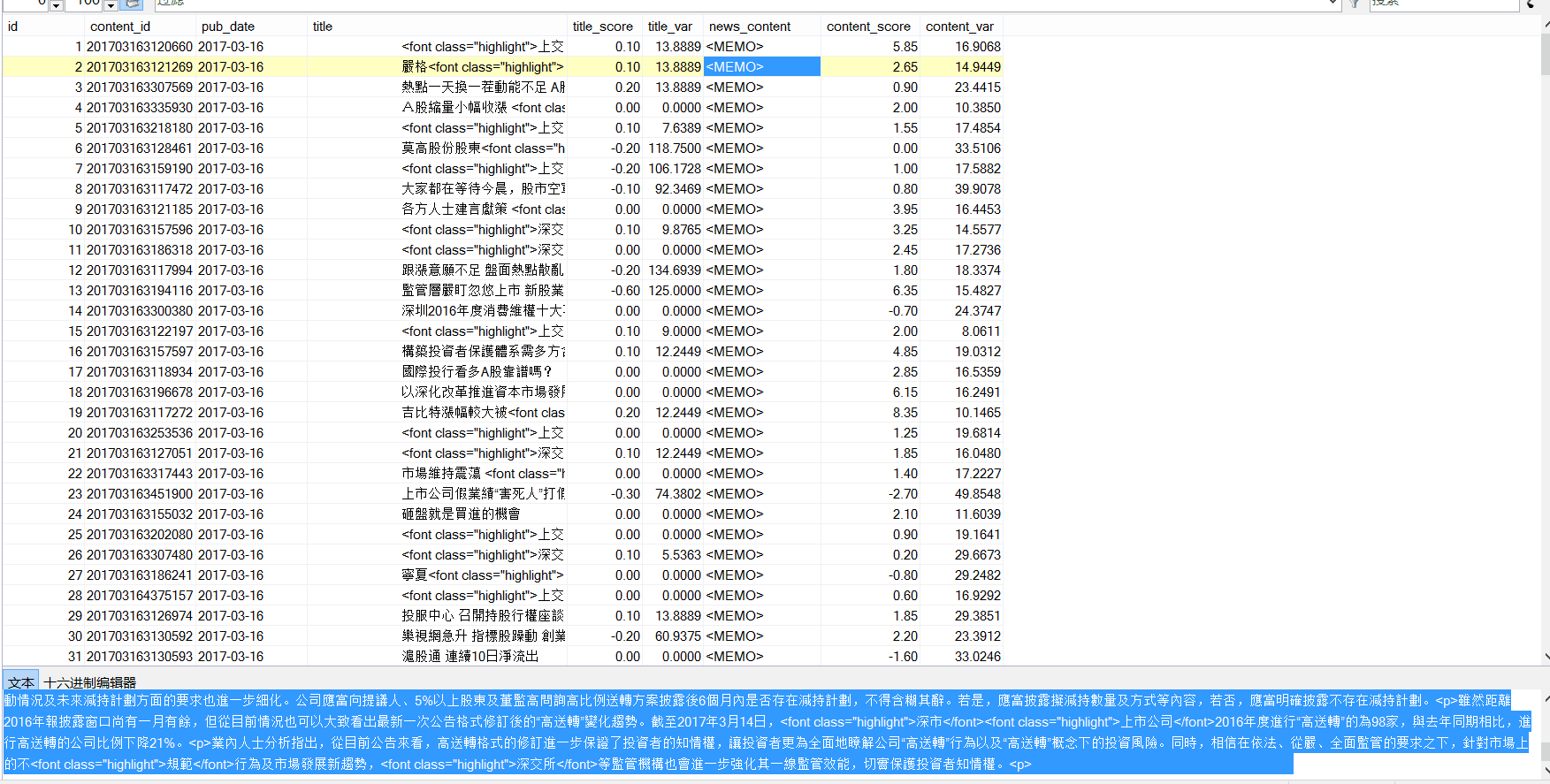
r_dict['news_content'] = cht_to_chs(tem[5])
r_dict['content_score'] = tem[6]
for key in stock_dict.keys():
#能找到對應的股票
if stock_dict[key][1] and ( r_dict['title'].find(stock_dict[key][1])!=-1 or r_dict['news_content'].find(stock_dict[key][1])!=-1 ):
w_dict=dict()
w_dict['code'] = key
w_dict['english_name'] = stock_dict[key][0]
w_dict['cn_name'] = stock_dict[key][1]
#得到分數
if r_dict['title_score']:
w_dict['score']=r_dict['title_score']
else:
w_dict['score']=r_dict['content_score']
#開始寫入
try:
global max_process
cmd = "INSERT INTO dyx_stock_score%d VALUES ('%s', '%s' , %d , '%s' , '%s' , %.2f );" % \
(index%max_process ,r_dict['content_id'] ,r_dict['pub_date'] ,w_dict['code'] ,w_dict['english_name'] ,w_dict['cn_name'] ,w_dict['score'])
cursor.execute(cmd)
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
error = " [-]%d fail to write to SQL" % index
cursor.rollback()
log_error('error.log',error)
else:
print(" [+]%d succeed to write to SQL" % index)
cursor.close()
conn.close()
def main():
num = 238143#數據庫查詢拿到的總數
p = None
for index in range(1,num+1):
if index%max_process==1:
if p:
p.close()
p.join()
p = multiprocessing.Pool(max_process)
r_cmd = ('select id,content_id,pub_date,title,title_score,news_content,content_score from dyx_emotion_analysis where id = %d;' % (index))
p.apply_async(func = read_SQL_write,args=(r_host,r_port,r_user,r_passwd,r_db,r_charset,w_host,w_port,w_user,w_passwd,w_db,w_charset,r_cmd,index,))
if p:
p.close()
p.join()
