#####說明
因工作方面接觸到圖像處理這一塊,需要對手機攝像頭采集的原始幀做Rotate或者Scale,但無奈對此的了解少之又少,於是網上搜了一頓,完事后將最近所學總結一下,以方便之后的人別踩太多坑。
首先想要了解YUV為何物:[請猛戳我](https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa904813)
上面的鏈接中微軟已經寫的很詳細了,國內大部分文章都是翻譯這篇文章的,如果還有疑問的同學可以參考下面這些大神的博客:
- [最簡單的基於FFmpeg的libswscale的示例(YUV轉RGB)](http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/42134965)
- [圖文詳解YUV420數據格式](http://www.cnblogs.com/azraelly/archive/2013/01/01/2841269.htm)
- [ANDROID 高性能圖形處理](http://tangzm.com/blog/?p=18)
- [Android攝像頭開發:實時攝像頭視頻預覽幀的編碼問題(二)](http://blog.csdn.net/yanzi1225627/article/details/8626411)
---
看完上面的文章應該都會有所了解和認識了,因為在**Android SDK <= 20(Android5.0)**中Google支持的Camera Preview Callback的YUV常用格式有兩種:NV21 / YV12,在此針對這兩種格式做分析。
#####NV21:
引用一段微軟的敘述:
######4:2:0 Formats, 12 Bits per Pixel
>Four 4:2:0 12-bpp formats are recommended, with the following FOURCC codes:
- IMC2
- IMC4
- YV12
- NV12
In all of these formats, the chroma channels are subsampled by a factor of two in both the horizontal and vertical dimensions.
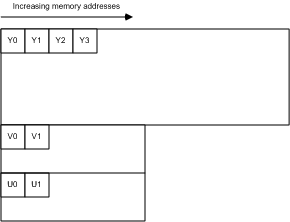
#####YV12
>`All of the Y samples appear first in memory as an array of unsigned char values.` This array is followed immediately by all of the V (Cr) samples. The stride of the V plane is half the stride of the Y plane, and the V plane contains half as many lines as the Y plane. The V plane is followed immediately by all of the U (Cb) samples, with the same stride and number of lines as the V plane (Figure 12).
**Figure 12:**
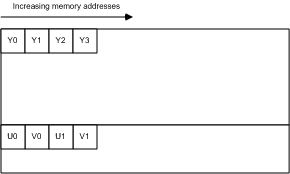
#####NV12
>`All of the Y samples are found first in memory as an array of unsigned char values with an even number of lines.` The Y plane is followed immediately by an array of unsigned char values that contains packed U (Cb) and V (Cr) samples, as shown in Figure 13. When the combined U-V array is addressed as an array of little-endian WORD values, the LSBs contain the U values, and the MSBs contain the V values. NV12 is the preferred 4:2:0 pixel format for DirectX VA. It is expected to be an intermediate-term requirement for DirectX VA accelerators supporting 4:2:0 video.
**Figure 13:**
從上可知YV12和NV12所占內存是**12bits/Pixel**,因為**每個Y就是一個像素點**,注意着色加粗的敘述,YUV值在內存中是按照數組的形式存放的,而由於**YV12和NV21都是屬於planar**格式,也就是Y值和UV值是獨立采樣的:
>``In a planar format, the Y, U, and V components are stored as three separate planes.``
既然Y、U、V值都是獨立的,那就意味着我們可以分別處理相應的值,比如在YV12中,排列方式是這樣的,**每4個Y共用一對UV值**,而U、V值又是按照如下格式排列
**下面是YV12格式中寬為16,高為4像素的排列**
|Y第一行: |Y Y|Y Y|Y Y|Y Y|
|:-----:|:--:|:--:|:--:| :--: |
|Y第二行:|Y Y|Y Y|Y Y|Y Y|
|Y第三行:|Y Y|Y Y|Y Y|Y Y|
|Y第四行:|Y Y|Y Y|Y Y|Y Y|
|V第一行:|V0|V1|V2|V3|
|U第一行:|U0|U1|U2|U3|
|V第二行:|V4|V5|V6|V7|
|U第二行:|U4|U5|U6|U7|
既然知道了YUV值的結構,我們就可以任性的對此圖像做Rotate,scale等等。這里我以480x270 (16:9)的一張原始幀圖像舉例,貼出部分代碼示例:
任意設定的一個帶有onPreviewFrame的類,**CameraPreviewFrame.java:**
/**
* 獲取preview的原始幀:
*
* 這里有個前提,因為Android camera preview默認格式為NV21的,所以需要
* 調用setPreviewFormat()方法設置為我們需要的格式
*
*/
@Override
public void onPreviewFrame(byte[] data, Camera camera) {// 假設這里的data為480x270原始幀
String SRC_FRAME_WIDTH = 480;
String SRC_FRAME_HEIGHT = 270;
String DES_FRAME_WIDTH = 480;
String DES_FRAME_HEIGHT = 270;
// 此處將data數組保存在了指定的路徑,保存類型為jpeg格式,但是普通的圖片瀏
// 覽器是無法打開的,需要使用RawView等專業的工具打開。
saveImageData(data);
// 定義與原始幀大小一樣的outputData,因為YUV420所占內存是12Bits/Pixel,
// 每個Y為一個像素8bit=1Byte,U=2bit=1/4(Byte),V=2bit=1/4(Byte),
// Y值數量為480*270,則U=V=480*270*(1/4)
byte[] outputData = new byte[DES_FRAME_WIDTH * DES_FRAME_HEIGHT * 3 / 2];
// call the JNI method to rotate frame data clockwise 90 degrees
YuvUtil.DealYV12(data, outputData, SRC_FRAME_WIDTH, SRC_FRAME_HEIGHT, 90);
saveImageData(outputData);
}
}
// save image to sdcard path: Pictures/MyTestImage/
public void saveImageData(byte[] imageData) {
File imageFile = getOutputMediaFile(MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE);
if (imageFile == null) {
return;
}
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(imageFile);
fos.write(imageData);
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "File not found: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "Error accessing file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static File getOutputMediaFile(int type) {
File imageFileDir = new File(Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES), "MyTestImage");
if (!imageFileDir.exists()) {
if (!imageFileDir.mkdirs()) {
Log.e(TAG, "can't makedir for imagefile");
return null;
}
}
// Create a media file name
String timeStamp = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd_HHmmss").format(new Date());
File imageFile;
if (type == MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE) {
imageFile = new File(imageFileDir.getPath() + File.separator +
"IMG_" + timeStamp + ".jpg");
} else if (type == MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
imageFile = new File(imageFileDir.getPath() + File.separator +
"VID_" + timeStamp + ".mp4");
} else {
return null;
}
return imageFile;
}
上面的代碼中可以看到調用了JNI的方法:**YuvUtil.RotateYV12()**
public class YuvUtil {
// 初始化,為data分配相應大小的內存
public static native void initYV12(int length, int scale_length);
public static native void DealYV12(byte[] src_data, byte[] dst_data, int width, int height, int rotation);
}
**com_example_jni_YuvUtil.h**
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include <jni.h>
/* Header for class _Included_com_example_jni_YuvUtil */
#ifndef _Included_com_example_jni_YuvUtil
#define _Included_com_example_jni_YuvUtil
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Class: com_example_jni_YuvUtil
* Method: initYV12
* Signature: (II)V
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_example_jni_YuvUtil_initYV12
(JNIEnv *, jclass, jint, jint);
/*
* Class: com_example_jni_YuvUtil
* Method: DealYV12
* Signature: ([B[BIIIII)V
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_example_jni_YuvUtil_DealYV12
(JNIEnv *, jclass, jbyteArray, jbyteArray, jint, jint, jint, jint, jint);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
**com_example_jni_YuvUtil.c**
#include "com_example_jni_YuvUtil.h"
#include <android/log.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <jni.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TAG "jni-log-jni" // 這個是自定義的LOG的標識
#define LOGD(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG,TAG ,__VA_ARGS__) // 定義LOGD類型
#define LOGI(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,TAG ,__VA_ARGS__) // 定義LOGI類型
#define LOGW(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_WARN,TAG ,__VA_ARGS__) // 定義LOGW類型
#define LOGE(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR,TAG ,__VA_ARGS__) // 定義LOGE類型
#define LOGF(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_FATAL,TAG ,__VA_ARGS__) // 定義LOGF類型
char *input_src_data, *output_src_data, *src_y_data,
*src_u_data, *src_v_data, *dst_y_data, *dst_v_data;
int src_data_width, src_data_height, len_src;
/*
* Class: com_example_jni_YuvUtil
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_example_jni_YuvUtil_initYV12
(JNIEnv *env, jclass jcls, jint length, jint scaleDataLength) {
len_src = length;
len_scale = scaleDataLength;
LOGD("########## len_src = %d, len_scale = %d \n", len_src, len_scale);
input_src_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * len_src);
LOGD("########## input_src_data = %d \n", input_src_data);
src_y_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * (len_src * 2 / 3));
src_u_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * (len_src / 6));
src_v_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * (len_src / 6));
dst_y_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * (len_src * 2 / 3));
dst_u_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * (len_src / 6));
dst_v_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * (len_src / 6));
}
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_example_jni_YuvUtil_DealYV12
(JNIEnv *env, jclass jcls, jbyteArray src_data,
jbyteArray dst_data, jint width, jint height, jint rotation, jint dst_width, jint dst_height) {
src_data_width = width;
src_data_height = height;
// 將src_data的數據傳給input_src_data
(*env)->GetByteArrayRegion (env, src_data, 0, len_src, (jbyte*)(input_src_data));
/*以下三個memcpy分別將Y、U、V值從src_data中提取出來,將YUV值分別scale或者rotate,則可得到對應格式的圖像數據*/
// get y plane
memcpy(src_y_data, input_src_data , (len_src * 2 /3));
// get u plane
memcpy(src_u_data, input_src_data + (len_src * 2 / 3), len_src / 6);
// get v plane
memcpy(src_v_data, input_src_data + (len_src * 5 / 6 ), len_src / 6);
/*獲取yuv三個值的數據可以做相應操作*/
// .........
// .........
// 例:將Y值置為0,則得到沒有灰度的圖像;
memset(input_src_data + src_data_width * src_data_height, 0, src_data_width * src_data_height);
// 將input_src_data的數據返回給dst_data輸出
// output to the dst_data
(*env)->SetByteArrayRegion (env, dst_data, 0, len_src, (jbyte*)(input_src_data));
}
/**
* free memory
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_example_jni_YuvUtil_ReleaseYV12
(JNIEnv *env , jclass jcls) {
free(output_src_data);
free(input_src_data);
}
**注意:以上代碼不是完全的,只是用於說明而已,如果需要更多的操作還請各位朋友自己完善,因為沒怎么寫過這類博客代碼很亂,如有表述的不清楚和有問題的地方,大家可以給我留言。**
