vue3組合式API
為什么要用組合式API,我們來看看它是如何解決vue2的局限性的
1.vue2的局限性
- 當組件內容越來越多,邏輯越來越復雜,可讀性就會降低,並且難以維護。
vue2組件采用配置式API,props,data,methods等相關的配置會被放在一起,導致同樣的功能塊分散,並和其他的功能塊混合。我們希望統一功能塊的代碼可以放在一起,增加可讀性
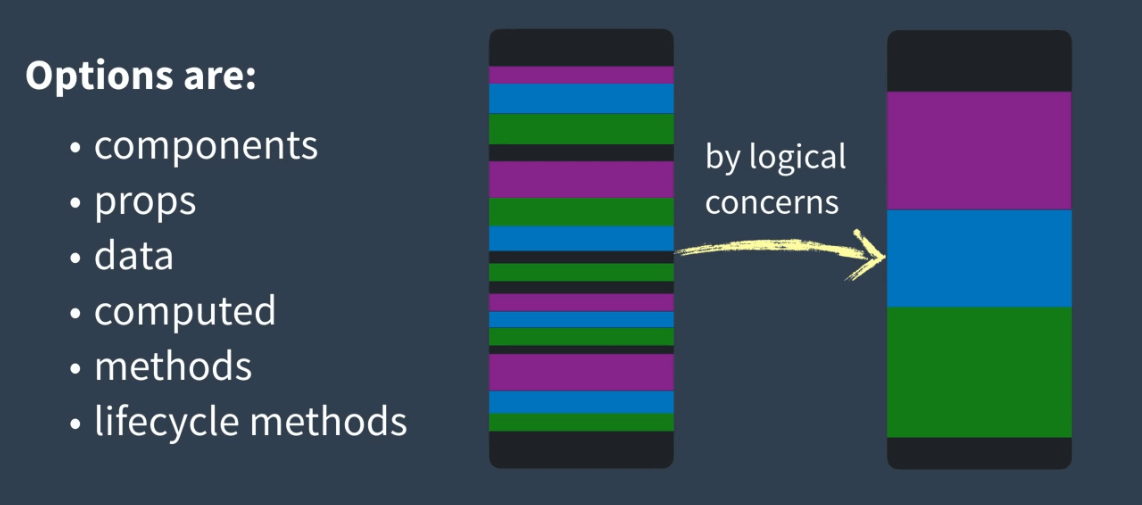
- vue2的代碼復用機制存在缺點,(Mixins)
- 容易沖突
- 依賴關系不明確,不易維護
- 函數式的mixins不能在實例化過程中使用
- vue2對ts的支持度不夠友好
2.組合式API的基本用法
組合式API是vue3新增的語法,它並沒有替代vue2的配置API,vue2原先的用法不變。組合式API只是更高級的語法
1. setup和ref方法
1<template>
2 <div>
3 <p>Capacity: {{ capacity }}</p>
4 <button @click="increaseCapacity()">Increase Capacity</button>
5 <h2>Attending</h2>
6 <ul>
7 <li v-for="(name, index) in attending" :key="index">{{ name }}</li>
8 </ul>
9 </div>
10</template>
11
12<script>
13import { ref } from "vue";
14export default {
15 setup() {
16 const capacity = ref(4);
17 function increaseCapacity() {
18 capacity.value++;
19 }
20 const attending = ref(["Tim", "Bob", "Joe"]);
21 return { capacity, attending, increaseCapacity };
22 }
23};
24</script>
使用ref創建響應式數據,模板中使用ref對象會自動結構[ref].value,不需要手寫.value
2. reactive和computed方法
1<template>
2 <p>Spaces Left: {{ spacesLeft }} out of {{ capacity }}</p>
3 <h2>Attending</h2>
4 <ul>
5 <li v-for="(name, index) in attending" :key="index">
6 {{ name }}
7 </li>
8 </ul>
9 <button @click="increaseCapacity()">Increase Capacity</button>
10</template>
11
12<script>
13import { reactive, computed, toRefs } from "vue";
14export default {
15 setup() {
16 const event = reactive({
17 capacity: 4,
18 attending: ["Tim", "Bob", "Joe"],
19 spacesLeft: computed(() => {
20 return event.capacity - event.attending.length;
21 })
22 });
23 function increaseCapacity() {
24 event.capacity++;
25 }
26 return { ...toRefs(event), increaseCapacity };
27 }
28};
29</script>
直接解構event會導致響應式失效,使用toRefs解構可以規避
3. 可復用的setup
1<template>
2 ...
3</template>
4<script>
5import useEventSpace from "@/use/event-space";
6import useMapping from "@/use/mapping";
7export default {
8 setup() {
9 return { ...useEventSpace(), ...useMapping() }
10 }
11};
12</script>
13
14<!-- event-space.js -->
15import { ref, computed } from "vue";
16export default function useEventSpace() {
17 const capacity = ref(4);
18 const attending = ref(["Tim", "Bob", "Joe"]);
19 const spacesLeft = computed(() => {
20 return capacity.value - attending.value.length;
21 });
22 function increaseCapacity() {
23 capacity.value++;
24 }
25 return { capacity, attending, spacesLeft, increaseCapacity };
26}
4. setup中的生命周期
- vue3中 beforeDestroy 和 destroyed 更名為 beforeUnmount 和 unmounted
- setup中使用生命周期函數需在函數前加on
- setup中不需要使用beforeCreate和created周期函數,- setup中函數的執行順序是 beforeCreate() -> setup() -> created()
- 新增兩個生命周期:onRenderTracked 和 onRenderTriggered
5. watch
1<template>
2 <div>
3 Search for <input v-model="searchInput" />
4 <div>
5 <p>Number of events: {{ results }}</p>
6 </div>
7 </div>
8</template>
9<script>
10import { ref, watch } from "@vue/composition-api";
11import eventApi from "@/api/event.js";
12export default {
13 setup() {
14 const searchInput = ref("");
15 const results = ref(0);
16 watch(() => {
17 results.value = eventApi.getEventCount(searchInput.value);
18 });
19 <span class="hljs-keyword">return</span> { searchInput, results };
20 }
21};
22</script>
23
24<!-- watch 傳參 -->
25watch(searchInput, (newVal, oldVal) => {
26 ...
27});
28watch([firstName, lastName], ([newFirst, newLast], [oldFirst, oldLast]) => {
29 ...
30});

