前言
前段時間,寫了面試必備的一系列文章,反應還不錯。有一些讀者反饋說,能不能整理一些面試常見的算法。前段時間,我恰好總結了 LeetCode 常見的面試算法題目。
Android 面試必備 - http 與 https 協議
Android 面試必備 - 計算機網絡基本知識(TCP,UDP,Http,https)
Android 面試必備 - 系統、App、Activity 啟動過程
面試官問, https 真的安全嗎,可以抓包嗎,如何防止抓包嗎
剛開始准備刷算法題目的時候,感覺真的是好難,十道題目有九道是不會的。心中曾一萬只草泥馬跑過,自己怎么這么辣雞。

慢慢得,我發現算法也是一個可以通過練習慢慢成長的。
- 首先我們要掌握基本的數據結構,數組,鏈表,哈希表, Set,二叉樹,堆,棧等。你要知道他們有什么優缺點,適應場景是什么,時間復雜度和空間復雜度是多少。而不能知道簡單的 API。
- 接着,掌握了這些基本的數據結構之后,一些基本的算法你也要掌握以下,比如快速排序,歸並排序,對排序,二分查找。這些基本的一定要掌握,面試當中經常也會問到。
- 分類刷題,我們在力扣上面可以看到,https://leetcode-cn.com/problemset/algorithms/ ,刷題是可以按標簽來的。比如鏈表,數組,二分查找,二叉樹,動態規划等
- 學好算法不是一日之功,需要長期的積累。建議的做法是每天做一兩道題,題目不在多,貴在於理解。堅持一兩個月,你會發現你的感覺逐漸好起來了
廢話不多說了,開始進入今天的正文,LeetCode鏈表知識點&題型總結
二叉樹的概念
二叉樹(Binary Tree)是包含n個節點的有限集合,該集合或者為空集(此時,二叉樹稱為空樹),或者由一個根節點和兩棵互不相交的、分別稱為根節點的左子樹和右子樹的二叉樹組成。
一棵典型的二叉樹如下圖所示:
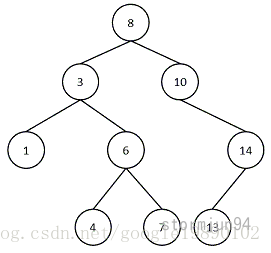
由上述的定義可以看出,二叉樹中的節點至多包含兩棵子樹,分別稱為左子樹和右子樹,而左子樹和右子樹又分別至多包含兩棵子樹。由上述的定義,二叉樹的定義是一種遞歸的定義。
二叉樹種類
滿二叉樹
對於一棵二叉樹,如果每一個非葉子節點都存在左右子樹,並且二叉樹中所有的葉子節點都在同一層中,這樣的二叉樹稱為滿二叉樹。
完全二叉樹
對於一棵具有n個節點的二叉樹按照層次編號,同時,左右子樹按照先左后右編號,如果編號為i的節點與同樣深度的滿二叉樹中編號為i的節點在二叉樹中的位置完全相同,則這棵二叉樹稱為完全二叉樹。
二叉排序樹:
又稱二叉查找樹(Binary Search Tree),亦稱二叉搜索樹。二叉排序樹或者是一棵空樹,或者是具有下列性質的二叉樹:
- 若左子樹不空,則左子樹上所有結點的值均小於它的根結點的值;
- 若右子樹不空,則右子樹上所有結點的值均大於或等於它的根結點的值;
- 左、右子樹也分別為二叉排序樹;
- 沒有鍵值相等的節點
二分查找的時間復雜度是O(log(n)),最壞情況下的時間復雜度是O(n)(相當於順序查找)
平衡二叉樹:
又稱 AVL 樹。平衡二叉樹是二叉搜索樹的進化版,所謂平衡二叉樹指的是,左右兩個子樹的高度差的絕對值不超過 1。
紅黑樹:
紅黑樹是每個節點都帶顏色的樹,節點顏色或是紅色或是黑色,紅黑樹是一種查找樹。紅黑樹有一個重要的性質,從根節點到葉子節點的最長的路徑不多於最短的路徑的長度的兩倍。對於紅黑樹,插入,刪除,查找的復雜度都是O(log N)。
哈夫曼樹:
給定n個權值作為n的葉子結點,構造一棵二叉樹,若帶權路徑長度達到最小,稱這樣的二叉樹為最優二叉樹,也稱為哈夫曼樹(Huffman tree)。
遍歷方式
二叉樹主要有四種遍歷方式
- 先序(先根)遍歷:即先訪問根節點,再訪問左孩子和右孩子
- 中序遍歷:先訪問做孩子,再訪問根節點和右孩子
- 后序遍歷:先訪問左孩子,再訪問右孩子,再訪問根節點
- 層次遍歷:按照所在層數,從下往上遍歷
前提:這里先給出測試中的二叉樹結構,如下圖所示
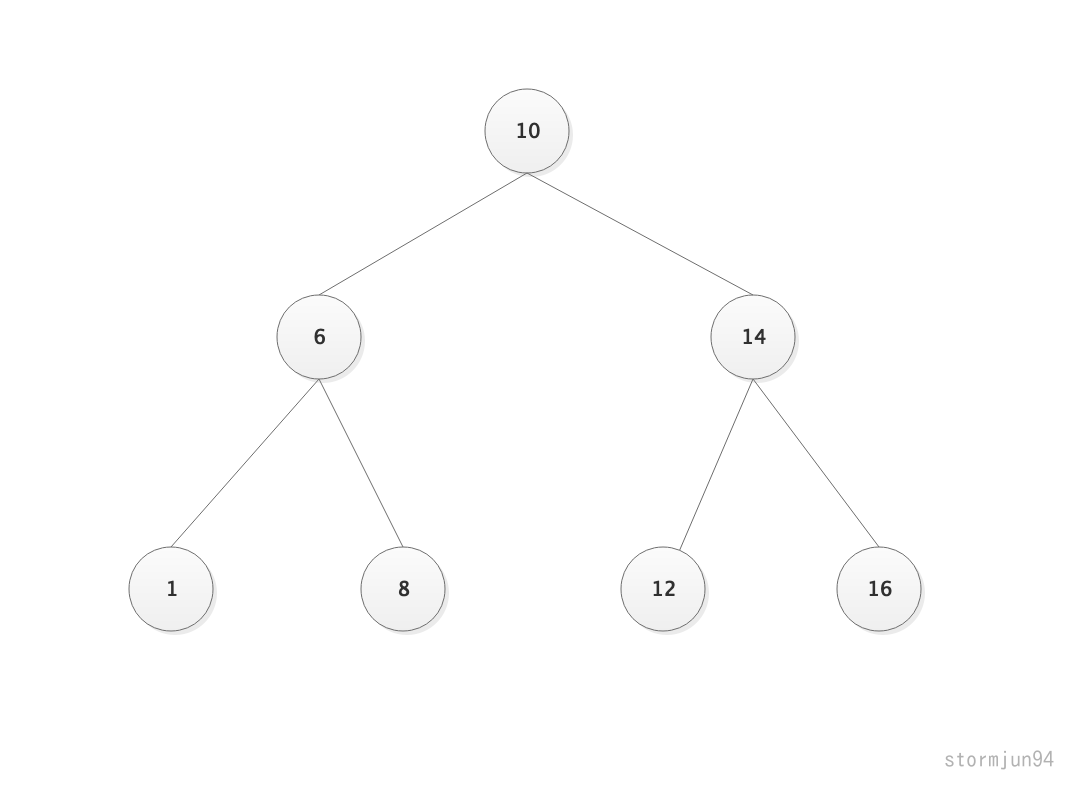
該二叉樹對應的幾種遍歷方式的結果順序:
- 先序遍歷:10->6->4->8->14->12->16
- 中序遍歷:4->6->8->10->12->14->16
- 后序遍歷:4->8->6->12->16->14->10
- 層次遍歷:10->6->14->4->8->12->16
遞歸
一棵樹要么是空樹,要么有兩個指針,每個指針指向一棵樹。樹是一種遞歸結構,很多樹的問題可以使用遞歸來處理。
1. 樹的高度
1.0 求二叉樹的最大層數(最大深度)
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree (Easy)
這道題目的解法其實很簡單
- 如果二叉樹為空,二叉樹的深度為0
- 如果二叉樹不為空,二叉樹的深度 = max(左子樹深度, 右子樹深度) + 1
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
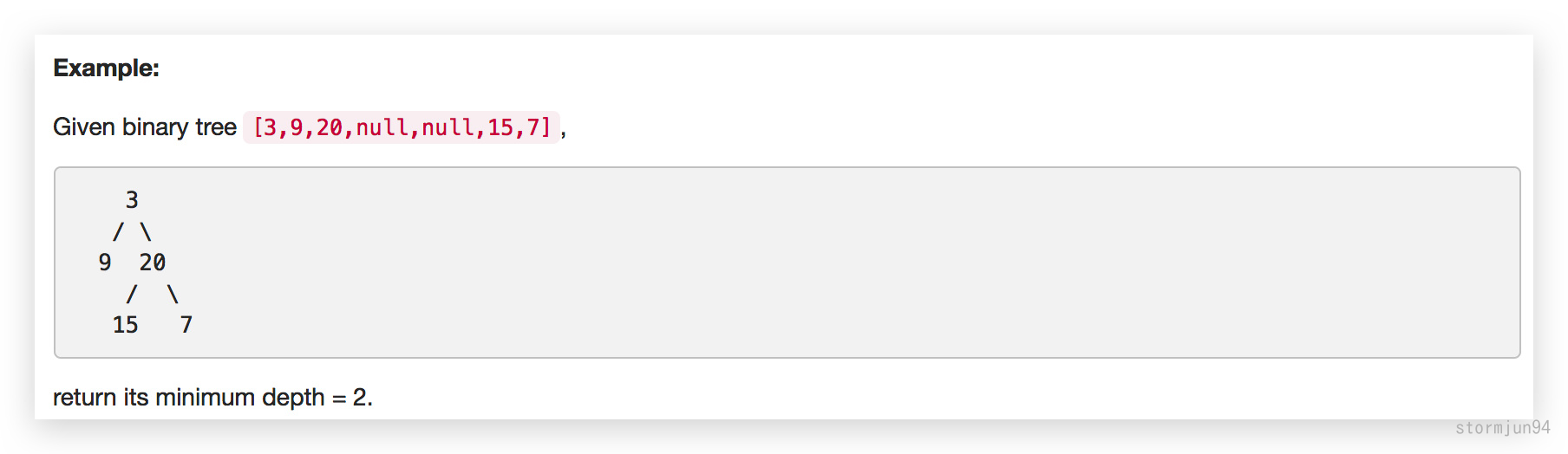
1.1 二叉樹的最小深度
LeetCode:Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
給定一個二叉樹,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是從根節點到最近葉子節點的最短路徑上的節點數量。
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
return (left == 0 || right == 0) ? left + right + 1 : Math.min(left, right) + 1;
}
}
2. 平衡樹
110. Balanced Binary Tree (Easy)
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
思路
平衡樹左右子樹高度差都小於等於 1
private boolean result = true;
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
maxDepth(root);
return result;
}
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int l = maxDepth(root.left);
int r = maxDepth(root.right);
if (Math.abs(l - r) > 1) result = false;
return 1 + Math.max(l, r);
}
3. 兩節點的最長路徑
543. Diameter of Binary Tree (Easy)
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
Return 3, which is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
private int max = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
depth(root);
return max;
}
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int leftDepth = depth(root.left);
int rightDepth = depth(root.right);
max = Math.max(max, leftDepth + rightDepth);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
4. 翻轉樹
226. Invert Binary Tree (Easy)
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode left = root.left; // 后面的操作會改變 left 指針,因此先保存下來
root.left = invertTree(root.right);
root.right = invertTree(left);
return root;
}
5. 歸並兩棵樹
617. Merge Two Binary Trees (Easy)
Input:
Tree 1 Tree 2
1 2
/ \ / \
3 2 1 3
/ \ \
5 4 7
Output:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
5 4 7
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return null;
if (t1 == null) return t2;
if (t2 == null) return t1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
root.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
root.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
return root;
}
6. 判斷路徑和是否等於一個數
Leetcdoe : 112. Path Sum (Easy)
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
return true, as there exist a root-to-leaf path 5->4->11->2 which sum is 22.
路徑和定義為從 root 到 leaf 的所有節點的和。
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return false;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == sum) return true;
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
7. 統計路徑和等於一個數的路徑數量
437. Path Sum III (Easy)
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8
10
/ \
5 -3
/ \ \
3 2 11
/ \ \
3 -2 1
Return 3. The paths that sum to 8 are:
1. 5 -> 3
2. 5 -> 2 -> 1
3. -3 -> 11
路徑不一定以 root 開頭,也不一定以 leaf 結尾,但是必須連續。
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int ret = pathSumStartWithRoot(root, sum) + pathSum(root.left, sum) + pathSum(root.right, sum);
return ret;
}
private int pathSumStartWithRoot(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int ret = 0;
if (root.val == sum) ret++;
ret += pathSumStartWithRoot(root.left, sum - root.val) + pathSumStartWithRoot(root.right, sum - root.val);
return ret;
}
8. 子樹
572. Subtree of Another Tree (Easy)
Given tree s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
Given tree t:
4
/ \
1 2
Return true, because t has the same structure and node values with a subtree of s.
Given tree s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
/
0
Given tree t:
4
/ \
1 2
Return false.
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (s == null) return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(s, t) || isSubtree(s.left, t) || isSubtree(s.right, t);
}
private boolean isSubtreeWithRoot(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (t == null && s == null) return true;
if (t == null || s == null) return false;
if (t.val != s.val) return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(s.left, t.left) && isSubtreeWithRoot(s.right, t.right);
}
9. 樹的對稱
101. Symmetric Tree (Easy)

public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return isSymmetric(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
if (t1.val != t2.val) return false;
return isSymmetric(t1.left, t2.right) && isSymmetric(t1.right, t2.left);
}
10 求二叉樹的鏡像
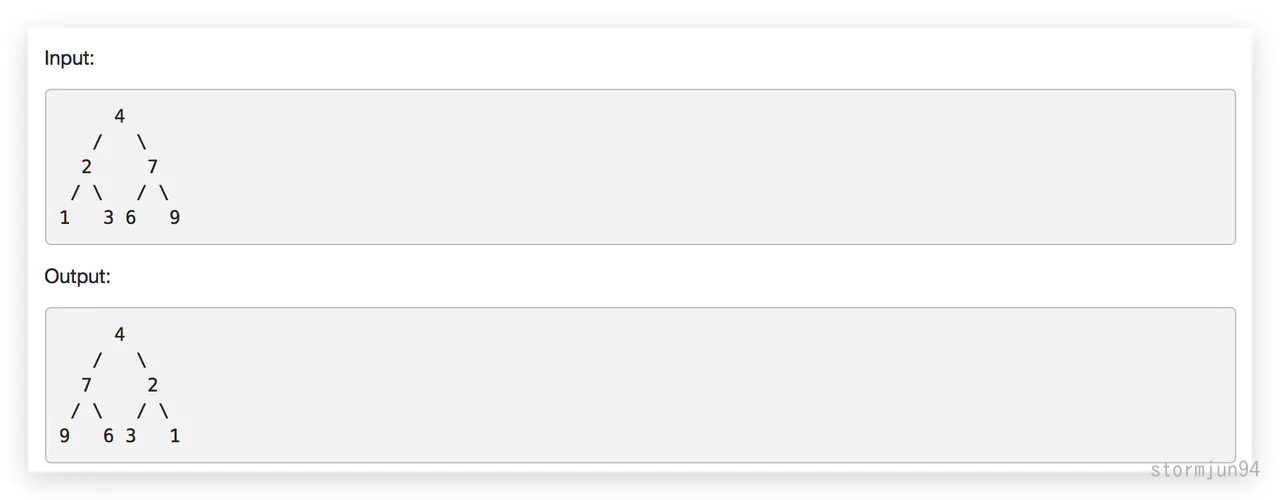
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return root;
// 先保存最節點,因為 invertTree 已經變化了
TreeNode node = root.left;
root.left = invertTree(root.right);
root.right = invertTree(node);
return root;
}
}
11. 最小路徑
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree (Easy)
樹的根節點到葉子節點的最小路徑長度
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
if (left == 0 || right == 0) return left + right + 1;
return Math.min(left, right) + 1;
}
層次遍歷
使用 BFS 進行層次遍歷。不需要使用兩個隊列來分別存儲當前層的節點和下一層的節點,因為在開始遍歷一層的節點時,當前隊列中的節點數就是當前層的節點數,只要控制遍歷這么多節點數,就能保證這次遍歷的都是當前層的節點。
1. 二叉樹的層序遍歷
給定二叉樹,返回其節點值的自下而上級別順序遍歷。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null)
return res;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int count = queue.size();
List<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0; i<count; i++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
temp.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
queue.add(node.right);
}
// 每次都添加到第一個位置
res.add(0, temp);
}
return res;
}
}
按之字形打印二叉樹
請實現一個函數按照之字形打印二叉樹,即第一行按照從左到右的順序打印,第二層按照從右至左的順序打印,第三行按照從左到右的順序打印,其他行以此類推。
- 設兩個棧,s2存放奇數層,s1存放偶數層
- 遍歷s2節點的同時按照左子樹、右子樹的順序加入s1,
- 遍歷s1節點的同時按照右子樹、左子樹的順序加入s2
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
/*
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> >();
Stack<TreeNode> s1 = new Stack<TreeNode>();
Stack<TreeNode> s2 = new Stack<TreeNode>();
int flag = 1;
if(pRoot == null)
return res;
s2.push(pRoot);
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty()){
if(flag % 2 != 0){
while(!s2.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = s2.pop();
temp.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
s1.push(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
s1.push(node.right);
}
}
}
if(flag % 2 == 0){
while(!s1.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = s1.pop();
temp.add(node.val);
if(node.right != null){
s2.push(node.right);
}
if(node.left != null){
s2.push(node.left);
}
}
}
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
temp.clear();
flag ++;
}
return res;
}
}
前中后序遍歷
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6
- 層次遍歷順序:[1 2 3 4 5 6]
- 前序遍歷順序:[1 2 4 5 3 6]
- 中序遍歷順序:[4 2 5 1 3 6]
- 后序遍歷順序:[4 5 2 6 3 1]
層次遍歷使用 BFS 實現,利用的就是 BFS 一層一層遍歷的特性;而前序、中序、后序遍歷利用了 DFS 實現。
前序、中序、后序遍只是在對節點訪問的順序有一點不同,其它都相同。
① 前序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
visit(root);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
② 中序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root.left);
visit(root);
dfs(root.right);
}
③ 后序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
visit(root);
}
1. 非遞歸實現二叉樹的前序遍歷
144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal (Medium)
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node == null) continue;
ret.add(node.val);
stack.push(node.right); // 先右后左,保證左子樹先遍歷
stack.push(node.left);
}
return ret;
}
2. 非遞歸實現二叉樹的后序遍歷
145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal (Medium)
前序遍歷為 root -> left -> right,后序遍歷為 left -> right -> root。可以修改前序遍歷成為 root -> right -> left,那么這個順序就和后序遍歷正好相反。
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node == null) continue;
ret.add(node.val);
stack.push(node.left);
stack.push(node.right);
}
Collections.reverse(ret);
return ret;
}
3. 非遞歸實現二叉樹的中序遍歷
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Medium)
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ret;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
ret.add(node.val);
cur = node.right;
}
return ret;
}
BST
二叉查找樹(BST):根節點大於等於左子樹所有節點,小於等於右子樹所有節點。
二叉查找樹中序遍歷有序。
1. 修剪二叉查找樹
669. Trim a Binary Search Tree (Easy)
Input:
3
/ \
0 4
\
2
/
1
L = 1
R = 3
Output:
3
/
2
/
1
題目描述:只保留值在 L ~ R 之間的節點
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int L, int R) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root.val > R) return trimBST(root.left, L, R);
if (root.val < L) return trimBST(root.right, L, R);
root.left = trimBST(root.left, L, R);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, L, R);
return root;
}
2. 尋找二叉查找樹的第 k 個元素
230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST (Medium)
中序遍歷解法:
private int cnt = 0;
private int val;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrder(root, k);
return val;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node, int k) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left, k);
cnt++;
if (cnt == k) {
val = node.val;
return;
}
inOrder(node.right, k);
}
遞歸解法:
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
int leftCnt = count(root.left);
if (leftCnt == k - 1) return root.val;
if (leftCnt > k - 1) return kthSmallest(root.left, k);
return kthSmallest(root.right, k - leftCnt - 1);
}
private int count(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
return 1 + count(node.left) + count(node.right);
}
3. 把二叉查找樹每個節點的值都加上比它大的節點的值
Convert BST to Greater Tree (Easy)
Input: The root of a Binary Search Tree like this:
5
/ \
2 13
Output: The root of a Greater Tree like this:
18
/ \
20 13
先遍歷右子樹。
private int sum = 0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
traver(root);
return root;
}
private void traver(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
traver(node.right);
sum += node.val;
node.val = sum;
traver(node.left);
}
4. 二叉查找樹的最近公共祖先
235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree (Easy)
_______6______
/ \
___2__ ___8__
/ \ / \
0 4 7 9
/ \
3 5
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes 2 and 8 is 6. Another example is LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return root;
}
5. 二叉樹的最近公共祖先
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree (Medium)
_______3______
/ \
___5__ ___1__
/ \ / \
6 2 0 8
/ \
7 4
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes 5 and 1 is 3. Another example is LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left == null ? right : right == null ? left : root;
}
6. 從有序數組中構造二叉查找樹
108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree (Easy)
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return toBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode toBST(int[] nums, int sIdx, int eIdx){
if (sIdx > eIdx) return null;
int mIdx = (sIdx + eIdx) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mIdx]);
root.left = toBST(nums, sIdx, mIdx - 1);
root.right = toBST(nums, mIdx + 1, eIdx);
return root;
}
7. 根據有序鏈表構造平衡的二叉查找樹
109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree (Medium)
Given the sorted linked list: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);
ListNode preMid = preMid(head);
ListNode mid = preMid.next;
preMid.next = null; // 斷開鏈表
TreeNode t = new TreeNode(mid.val);
t.left = sortedListToBST(head);
t.right = sortedListToBST(mid.next);
return t;
}
private ListNode preMid(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
ListNode pre = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return pre;
}
8. 在二叉查找樹中尋找兩個節點,使它們的和為一個給定值
653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST (Easy)
Input:
5
/ \
3 6
/ \ \
2 4 7
Target = 9
Output: True
使用中序遍歷得到有序數組之后,再利用雙指針對數組進行查找。
應該注意到,這一題不能用分別在左右子樹兩部分來處理這種思想,因為兩個待求的節點可能分別在左右子樹中。
public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root, nums);
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = nums.get(i) + nums.get(j);
if (sum == k) return true;
if (sum < k) i++;
else j--;
}
return false;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> nums) {
if (root == null) return;
inOrder(root.left, nums);
nums.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right, nums);
}
9. 在二叉查找樹中查找兩個節點之差的最小絕對值
530. Minimum Absolute Difference in BST (Easy)
Input:
1
\
3
/
2
Output:
1
利用二叉查找樹的中序遍歷為有序的性質,計算中序遍歷中臨近的兩個節點之差的絕對值,取最小值。
private int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private TreeNode preNode = null;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
return minDiff;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left);
if (preNode != null) minDiff = Math.min(minDiff, node.val - preNode.val);
preNode = node;
inOrder(node.right);
}
10. 尋找二叉查找樹中出現次數最多的值
501. Find Mode in Binary Search Tree (Easy)
1
\
2
/
2
return [2].
答案可能不止一個,也就是有多個值出現的次數一樣多。
private int curCnt = 1;
private int maxCnt = 1;
private TreeNode preNode = null;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> maxCntNums = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root, maxCntNums);
int[] ret = new int[maxCntNums.size()];
int idx = 0;
for (int num : maxCntNums) {
ret[idx++] = num;
}
return ret;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> nums) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left, nums);
if (preNode != null) {
if (preNode.val == node.val) curCnt++;
else curCnt = 1;
}
if (curCnt > maxCnt) {
maxCnt = curCnt;
nums.clear();
nums.add(node.val);
} else if (curCnt == maxCnt) {
nums.add(node.val);
}
preNode = node;
inOrder(node.right, nums);
}
參考文章
小結
如果你想學好算法,建議上面二叉樹的題目都刷一下。如果你只是想應付面試,主要看一下高頻的面試題目即可。
- 樹的遞歸。比如樹的深度,最小深度,樹的鏡像。
- 二叉樹的前序遍歷,中序遍歷,后續遍歷,記住,遞歸和非遞歸解法都要會。學會舉一反三。
- 二叉樹的層序遍歷,遞歸和非遞歸也都要會。
- 常見的 BST 算法。二叉查找樹的最近公共祖先(兩個元素的,三個元素的,多個元素呢)。二叉樹的最近公共祖先。
如果你覺得對你有所幫助,請幫忙 start
Android_interview github。或者關注我的微信公眾號徐公碼字

