本篇內容比較干澀,請自備礦泉水
文章分6個主題進行講解
- PHP運行機制和原理
- PHP底層變量數據結構
- PHP傳值賦值中的COW特性
- PHP垃圾回收機制
- PHP中數組底層分析
- PHP數組函數分類
PHP運行機制和原理
掃描 -> 解析 -> 編譯 -> 執行 -> 輸出
執行步驟
- 掃描
對代碼進行詞法和語法分析,將內容切割成一個個片段 (token)
- 解析
將代碼片段篩掉空格注釋等,將剩下的token 轉成有意義的表達式
- 編譯
將表達式編譯成中間碼 (opcode)
- 執行
將中間碼一條條執行
- 輸出
將執行結果輸出到緩沖區
代碼切割
$code = <<<EOF
<?php
echo 'hello world'l;
$data = 1+1;
echo $data;
EOF;
print_r(token_get_all($code));
執行結果
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[0] => 376
[1] => <?php
[2] => 1
)
[1] => Array
(
[0] => 319
[1] => echo
[2] => 2
)
[2] => Array
(
[0] => 379
[1] =>
[2] => 2
)
[3] => Array
(
[0] => 318
[1] => 'hello world'
[2] => 2
)
[4] => Array
(
[0] => 310
[1] => l
[2] => 2
)
[5] => ;
[6] => Array
(
[0] => 379
[1] =>
[2] => 2
)
[7] => =
[8] => Array
(
[0] => 379
[1] =>
[2] => 3
)
[9] => Array
(
[0] => 308
[1] => 1
[2] => 3
)
[10] => +
[11] => Array
(
[0] => 308
[1] => 1
[2] => 3
)
[12] => ;
[13] => Array
(
[0] => 379
[1] =>
[2] => 3
)
[14] => Array
(
[0] => 319
[1] => echo
[2] => 4
)
[15] => Array
(
[0] => 379
[1] =>
[2] => 4
)
[16] => ;
)
觀察上面可以得到三個信息
- Token id 例如空格回車都是 379
- token 字符串
- 行號
Token id 是Zend內部token對應碼, 定義於zend_language_parser.h
提高PHP執行效率
- 壓縮代碼,去除無用注釋和空白字符 (jquery.min.js)
- 盡量使用PHP內置函數或擴展函數
- 用 apc/xcache/opcache 等緩存PHP的opcode
- 緩存復雜和耗時的運算結果
- 能異步處理的不要同步處理,如發送郵件
- HHVM 為何速度快
通過虛擬機(類似java) 直接將PHP轉換成二進制字節碼運行,執行時不用每次都去解析。
PHP底層變量數據結構
使用 zval 結構體保存,下面代碼在 Zend/zend.h 定義
typedef union _zvalue_value
{
/* 下面定義描述了PHP的8大數據類型 */
long lval; // 長整型 布爾型
double dval; // 浮點型
struct { // 字符串型
char *val;
int len; // strlen 返回這個值
} str; // NULL 類型表示本身為空
HashTable *ht; // 數組使用哈希表實現
zend_object_value obj; // 對象類型
} zvalue_value;
struct _zval_struct
{
zvalue_value value; /* 變量的值 */
zend_uint refcount__gc;
zend_uchar type; /* 變量的類型 */
zend_uchar is_ref__gc
};
typedef struct _zval_struct zval;
變量類型的定義,下面代碼在 Zend/zend_types.h 定義
typedef unsigned int zend_uint;
typedef unsigned char zend_uchar;
PHP數據8大類型統一通過 zvalue_value 聯合體存儲
聯合體自身為空 描述 null
long 描述 int bool
double 描述 float
str 描述 string
HashTable 描述 數字數組和關聯數組
zend_object_value 描述 對象和資源
PHP變量類型描述使用 zend_uchar type 描述
#define IS_NULL 0
#define IS_LONG 1
#define IS_DOUBLE 2
#define IS_BOOL 3
#define IS_ARRAY 4
#define IS_OBJECT 5
#define IS_STRING 6
#define IS_RESOURCE 7
#define IS_CONSTANT 8
#define IS_CONSTANT_ARRAY 9
例如 $a=3 結構體如下(偽代碼)
struct {
zvalue_value = 3;
refcount__gc = 1;
type = IS_LONG;
is_ref__gc = 0;
}
$a 就像指針一樣指向上面的結構體
PHP傳值賦值中的COW特性
在 _zval_struct 數據結構中還有下面兩個成員
- zend_uint refcount__gc 表示被引用多少次,每次引用+1
- zend_uchar is_ref__gc 表示普通變量還是引用變量
下面通過編寫代碼了解引用機制
此處我使用的是 php5.4,需要安裝 xdebug 來查看變量引用
注意使用 php7.2 測試的時候引用數會一直為0
編譯生成 xdebug.so
yum -y install php-devel
tar xf xdebug-2.8.0alpha1.tgz
cd xdebug-2.8.0alpha1
phpize
find /usr/ -name "php-config"
./configure --with-php-config=/usr/bin/php-config
make && make install
ls /usr/lib64/php/modules/
配置 xdebug
php --ini
echo 'zend_extension=/usr/lib64/php/modules/xdebug.so' >> /etc/php.ini
systemctl restart php72-php-fpm.service
php -m | grep xdebug
編寫測試代碼
$a = 3;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
輸出
a: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=3
refcount引用數為1is_ref為0表示普通變量=3表示值為3
開始引用
$a = 3;
$b = $a;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');
輸出
a: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=3
b: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=3
賦予新值
$a = 3;
$b = $a;
$b = 5;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');
輸出
a: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=3
b: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=5
傳遞地址
$a = 3;
$b = &$a;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');
輸出
a: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=3
b: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=3
is_ref 該變量從普通變量轉成引用變量
賦予新值
$a = 3;
$b = &$a;
$c = $a;
$b = 5;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');
xdebug_debug_zval('c');
a: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=5
b: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=5
c: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=3
總結
-
變量之間傳值是通過引用賦值形式,無需開辟新的空間,節省資源
-
當一個變量的值發生改變時,會復制一份來存新的值,取消引用,稱為 copy on write (COW)
-
引用變量不會觸發COW
PHP垃圾回收機制
什么是垃圾
上海人: 你算什么垃圾?
如果一個zval 沒有任何變量引用它,那它就是垃圾
?: (refcount=0, is_ref=0)=5
為啥要清理垃圾?
有人說php線程結束時會銷毀所有變量,關閉所有句柄資源,不是自動的嘛,為啥要清理
- 如果php 短時間內處理多個大文件時(如1G的電影),處理完不回收繼續處理下一個,會造成內存溢出
- 如果php 是個守護進程或者長時間運行的腳本,不回收垃圾,慢慢積累會造成內存溢出
如何清理垃圾
- 找垃圾
- 清除
- 找垃圾
通過 get_defined_vars 查看所有已定義變量
底層代碼 zend_globals.h 定義了存儲所有變量的兩個哈希表
struct _zend_executor_globals {
...
HashTable *active_symbol_table; //局部變量符號表
HashTable symbol_table; //全局變量符號表
...
}
找到所有已定義的變量后,尋找哪些變量引用數為0
struct _zval_struct{
...
zend_uint refcount__gc;
zend_uchar is_ref__gc;
...
}
- 清理垃圾
如上面將 refcount__gc 為0的變量清除,這個思路是 PHP5.2版本之前的做法了
PHP5.3后用 引用計數系統中同步周期回收 算法來清除
其實新算法也是基於 refcount__gc 來回收,那么為什么要用新算法呢?
我們知道 refcount__gc 為0的一定是垃圾
但是並不是所有的垃圾 refcount__gc 都為0
也有 refcount__gc 不為0 的垃圾,如下實驗可以產生不為0的垃圾
一個例子
$a = ['a'];
$a[] = &$a; //引用自己
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
輸出
a: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=array (
0 => (refcount=1, is_ref=0)='a',
1 => (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=...
)
第二元素: ... 代表遞歸,引用數2,是一個指針引用變量
官方提供的一張圖
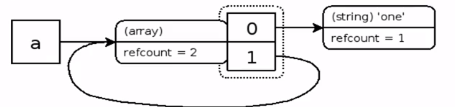
此時刪掉 $a
$a = ['a'];
$a[] = &$a;
unset($a);
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
輸出
a: no such symbol
因為 $a 被刪了,所以xdebug打印不出來,那么此時理論結構如下
(refcount=1, is_ref=1)=array (
0 => (refcount=1, is_ref=0)='a',
1 => (refcount=1, is_ref=1)=...
)
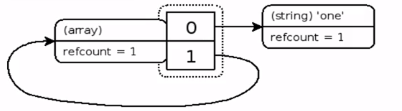
此時這個 zval 已經沒有符號 (symbol) 引用了,但是它因為自己引用自己 refcount 為1,所以它是一個奇葩的垃圾
對於此情況php腳本結束時,會自動清理,當結束前會占用空間
因此 5.2 版本之前的垃圾清理思路不能覆蓋這種情況
引用計數系統中同步周期回收算法 (Concurrent Cycle Collection in Reference Counted System)
繼續以上面代碼為例進行說明
新算法說明:
將 $a 作為疑似垃圾變量,進行模擬刪除 (refcount--),然后模擬恢復,恢復條件是有其他變量引用該值時才進行模擬恢復 (refcount++)
這樣沒能恢復成功的就是垃圾了,把它刪除即可。
例如上面的奇葩垃圾:
(refcount=1, is_ref=1)=array (
0 => (refcount=1, is_ref=0)='a',
1 => (refcount=1, is_ref=1)=...
)
模擬刪除后變成:
(refcount=0, is_ref=1)=array (
0 => (refcount=0, is_ref=0)='a',
1 => (refcount=0, is_ref=1)=...
)
然后模擬恢復:
因為沒有類似 $a 這種 symbol 取指向該zval,所以恢復不來
何時清除
通過上面的算法疑似垃圾會存放到一個區域(垃圾站),只有垃圾站滿了才會立刻清除。 注意前提是開啟垃圾回收
開啟垃圾回收兩種方式
-
php.ini 下的
zend.enable_gc = On默認開啟 -
通過
gc_enable()和gc_disable()來打開或關閉垃圾回收
可以直接使用 gc_collect_cycles() 函數強制執行周期回收
最后說了那么多,其實只需要了解其中的原理,整個過程不需要PHP開發人員參與,只需要調用 gc_enable() 或 gc_collect_cycles() 即可實現自動回收
PHP中數組底層分析
先復習一下數組特性
PHP 數組鍵的特性
$arr = [
1 => 'a',
'1' => 'b',
1.5 => 'c',
true => 'd',
];
print_r($arr);
Array
(
[1] => d
)
key 可以是 integer 或 string
value 可以是任意類型
key 有如下特性
- 數字字符串會被轉成整型 '1' => 1
- 浮點型和布爾型轉成整型 1.3 =》 1
- null會被當做空字符串 null => ''
- 鍵名不可以使用對象和數組
- 相同鍵名后面覆蓋前面
訪問數組元素
- $arr[key]
- $arr{key}
5.4 版本后可以使用如下
function getArr(){ return [1,2,3,4]; }
echo getArr()[2];
刪除數組元素
$a = [1,2,3,4];
foreach ($a as $k => $v) {
unset($a[$k]);
}
$a[] = 5;
print_r($a);
Array
(
[4] => 5
)
- 刪除不會重置索引
數組遍歷
- for
- foreach
- array_walk
- array_map
- current 和 next
數組內部實現
實現使用兩個結構 HashTable 和 bucket
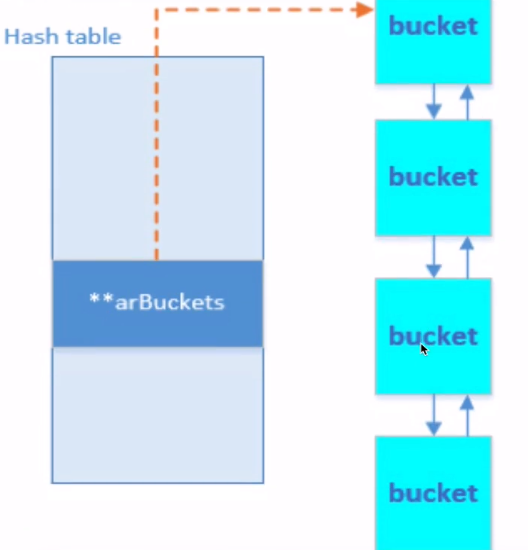
- 什么是 HashTable
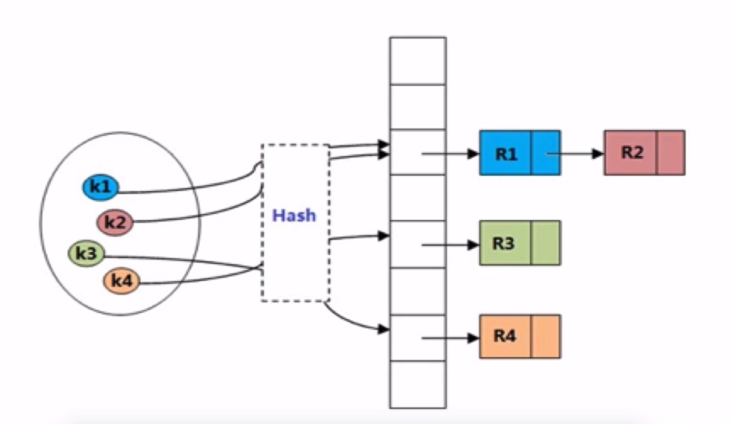
哈希表,通過關鍵字直接訪問內存存儲位置的數據結構。
通過把關鍵字進行哈希函數計算,得到映射到表中的位置使得: 查找,插入,修改,刪除均在O(1)完成
下面代碼在 Zend/zend_types.h
typedef struct _zend_array HashTable;
struct _zend_array {
zend_refcounted_h gc;
union {
struct {
ZEND_ENDIAN_LOHI_4(
zend_uchar flags,
zend_uchar nApplyCount,
zend_uchar nIteratorsCount,
zend_uchar consistency)
} v;
uint32_t flags;
} u;
uint32_t nTableMask;
Bucket *arData;
uint32_t nNumUsed;
uint32_t nNumOfElements;
uint32_t nTableSize;
uint32_t nInternalPointer;
zend_long nNextFreeElement;
dtor_func_t pDestructor;
};
舊版結構體
typedef struct _hashtable {
uint nTableSize;
uint nTableMask;
uint nNumOfElements;
ulong nNextFreeElement;
Bucket *pInternalPointer;
Bucket *pListHead;
Bucket *pListTail;
Bucket **arBuckets;
unsigned char nApplyCount;
};
| 成員 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| nTableSize | Bucket大小,最小為8,以2x增長 |
| nTableMask | 索引優化 nTableSize-1 |
| nNumOfElements | 元素個數 使用count()函數直接返回這個 |
| nNextFreeElement | 下一個索引位置 foreach使用 |
| pInternalPointer | 當前遍歷的指針,foreach比for快的原因,reset current函數使用 |
| pListHead | 存儲數組頭部指針 |
| pListTail | 存儲數組尾部指針 |
| arBuckets | 實際存儲容器 |
| arData | Bucket數據 |
| nApplyCount | 記錄被遞歸次數,防止死循環遞歸 |
typedef struct bucket
{
ulong h;
uint nKeyLength;
void *pData;
void *pDataPtr;
struct bucket *pListNext;
struct bucket *pListLast;
struct bucket *pNext;
struct bucket *pLast;
const char *arKey;
};
| 成員 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| h | 對char *key進行hash后的值,或是用戶指定數字索引值 |
| nKeyLength | 哈希關鍵字長度,若為索引數字則為0 |
| pData | 指向value 一般是用戶數據的副本,若為指針數據則指向指針 |
| pDataPtr | 如果是指針數據,指針會指向真正value,上面指向此 |
| pListNext | 整個hash表下個元素 |
| pListLast | 整個hash表上個元素 |
| pNext | 同一個hash的下一個元素 |
| pLast | 同一個hash的上一個元素 |
| arKey | 保存當前key對應的字符串 |
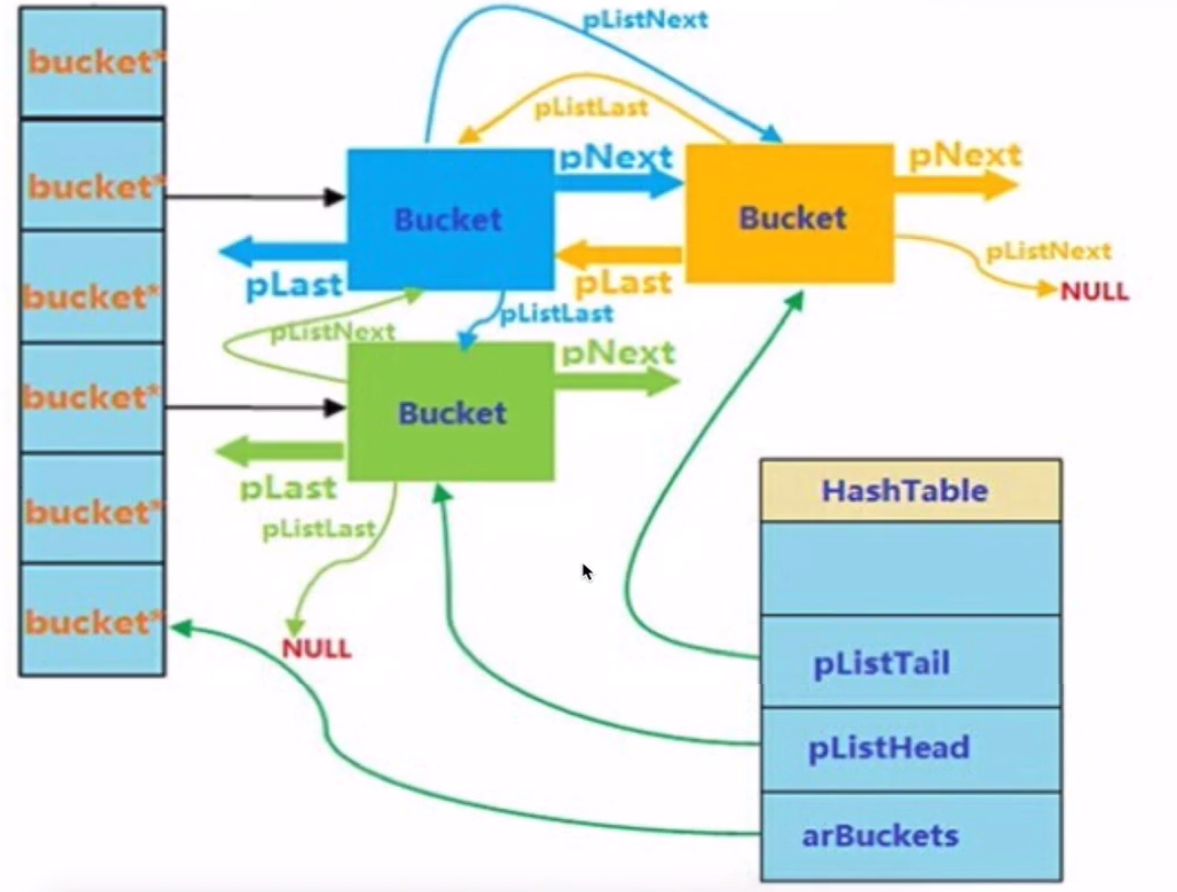
foreach 遍歷先從 HashTable 的 pListHead -> pListNext
pNext 和 pLast 用於hash沖突同一個hash不同個bucket之間指針
PHP數組函數分類
建議體驗一下下面的函數,不用記住,只是留個印象,當你需要用的時候會聯想起來的,而不用自己去實現
遍歷
- prev
- next
- current
- end
- reset
- each
排序
- sort
- rsort
- asort
- ksort
- krsort
- uasort
- uksort
查找
- in_array
- array_search
- array_key_exists
分合
- array_slice
- array_splice
- implode
- explode
- array_combine
- array_chunk
- array_keys
- array_values
- array_columns
集合
- array_merge
- array_diff
- array_diff_*
- array_intersect
- array_intersect_*
隊列/棧
- array_push
- array_pop
- array_shift
其他
- array_fill
- array_flip
- array_sum
- array_reverse
