來源博客:Wang Jie's Blog
本文鏈接:http://blog.wangjiegulu.com/2018/02/13/writing_a_modular_project_on_android
版權聲明:本博客所有文章除特別聲明外,均采用 CC BY 4.0 CN協議 許可協議。轉載請注明出處。
原文:https://medium.com/mindorks/writing-a-modular-project-on-android-304f3b09cb37
在Android上編寫模塊化項目(翻譯)
當我們在 Android Studio 上創建一個新的項目時,自帶一個 app module。這時我們大多數人編寫整個應用的地方。每次點擊 run 按鈕都會觸發我們整個所有 module 上的 gradle 構建,並檢查所有文件是否有變化。這就是為什么 gradle 構建會在更大的應用程序上花費 10分鍾的時間,並且減慢開發者的輸出。
要解決這個問題,復雜的應用程序,如 Uber 決定對它們的應用程序進行模塊化並從中獲得了很多。下面是試用模塊化項目的一些優勢:
- 更快的 gradle 構建
- 跨應用/模塊復用通用的功能
- 易於插拔到Instant apps
- 更好的團隊工作,一個人可以單獨負責一個模塊
- 更流暢地git flows
由於上述優勢,當我剛開始Posts這個應用時,我就在始終堅持使用模塊化方法。對此,Android 團隊已經給我們提供了一些工具,但是我確實遇到了一些障礙,一下是我學習到的內容:
我該怎么分割我的 modules ?
你的應用程序是流程集構成的,比如,Google Play 有應用詳情流,它包含了簡要,描述詳情,應用截圖,評論活動等。
所有這些都可以歸為同一模塊 —— app-details。
你的應用會包含多個類似流程的模塊,有 authentication, settings, on-boarding等等。當然還有一些不需要UI元素呈現的模塊如 —— notifications, analytics, first-fetch等等。這些模塊包含與流程有關的 activities, repositories, entities和依賴注入相關東西。
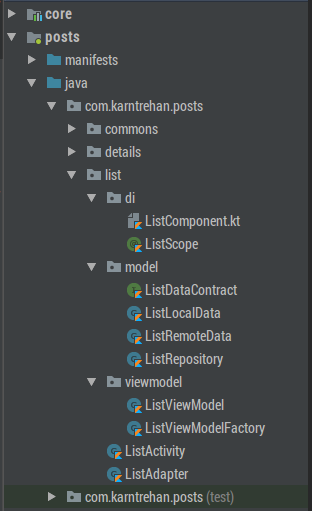
但是這些模塊中總是有一些共同的功能和工具。這就是為什么你需要一個 core 模塊。
什么是 core 模塊 ?
Core 模塊是一個你項目中簡單的 module 庫。core 庫可以(除其它外),
- 給你的依賴注入框架提供全局依賴,如 Retrofit, SharedPreferences等等。
- 包含工具類和擴展方法
- 包含全局類和回調
- 在 application 類中的初始化庫,如 Firebase Analytics,Crashlytics,LeakCanary,Stetho等等
怎么使用第三方庫?
核心(core)模塊的其中一個職責是為你的功能(feature)模塊提供外部依賴。這使得很容易實現在你的 feature 模塊中共享相同版本的庫。只需要在你的 core 模塊的 dependencies 中使用 api,這樣你就能在所有 feature 模塊中使用它們。
dependencies {
api fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
api deps.support.appCompat
api deps.support.recyclerView
api deps.support.cardView
api deps.support.support
api deps.support.designSupport
api deps.android.lifecycleExt
api deps.android.lifecycleCommon
api deps.android.roomRuntime
api deps.android.roomRx
api deps.kotlin.stdlib
api deps.reactivex.rxJava
api deps.reactivex.rxAndroid
api deps.google.dagger
kapt deps.google.daggerProcessor
api deps.square.picasso
api deps.square.okhttpDownloader
api deps.square.retrofit
api deps.square.okhttp
api deps.square.gsonConverter
api deps.square.retrofitRxAdapter
implementation deps.facebook.stetho
implementation deps.facebook.networkInterceptor
testApi deps.test.junit
androidTestApi deps.test.testRunner
androidTestApi deps.test.espressoCore
}
有種依賴的可能性是只有對 feature-a 模塊有用,但是在 feature-b 中無用。對於這種情況,我推薦在你的 core 的依賴中使用 api,因為 proguard 注意到而不會包含在 feature-b instant app 中。
怎么使用 Room ?
這個困擾我挺久的時間。我們希望把我們的數據庫定義到 core 模塊中,因為它是我們應用程序要共享的通用的功能。為了讓 Room 工作,你需要一個包含了所有 entity 類的數據庫文件。
@Database(entities = [Post::class, User::class, Comment::class], version = 1,exportSchema = false)
abstract class PostDb : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun postDao(): PostDao
abstract fun userDao(): UserDao
abstract fun commentDao(): CommentDao
}
但是,如上面提到的,我們的 entity 類是被定義在 feature 模塊中,而且 core 模塊不能去訪問它們。這是我碰到障礙的地方,經過一番思考后,你做了一件最棒的事,尋求 Yigit 的幫助。
Yigit 闡明了觀點,你必須要在每個 feature模塊中都創建一個新的 db 文件,然后每個模塊一個數據庫。
這有幾個好處:
- 遷移是模塊化的
- 即時 app 僅包含它們需要的表
- 查詢會更快
缺點:
- 跨模塊數據關系將不可能
注意:為了 Room 的注解能夠工作,不要忘記在你的 feature 模塊中增加下面依賴
kapt "android.arch.persistence.room:compiler:${versions.room}"
怎么使用 Dagger 2 ?
同樣的問題 Dagger 也遇到了。我的 core 模塊中的 application 類不能訪問和初始化我 feature 模塊中的組件。這是從屬組件完美的用例。
你的 core 組件定義了它想要暴露給依賴組件的依賴關系
@Singleton
@Component(modules = [AppModule::class, NetworkModule::class, StorageModule::class, ImageModule::class])
interface CoreComponent {
fun context(): Context
fun retrofit(): Retrofit
fun picasso(): Picasso
fun sharedPreferences(): SharedPreferences
fun scheduler(): Scheduler
}
您的模塊組件將 CoreComponent 定義為依賴項,並使用傳遞的依賴
@ListScope
@Component(dependencies = [CoreComponent::class], modules = [ListModule::class])
interface ListComponent {
fun inject(listActivity: ListActivity)
}
@Module
@ListScope
class ListModule {
/*Uses parent's provided dependencies like Picasso, Context and Retrofit*/
@Provides
@ListScope
fun adapter(picasso: Picasso): ListAdapter = ListAdapter(picasso)
@Provides
@ListScope
fun postDb(context: Context): PostDb = Room.databaseBuilder(context, PostDb::class.java, Constants.Posts.DB_NAME).build()
@Provides
@ListScope
fun postService(retrofit: Retrofit): PostService = retrofit.create(PostService::class.java)
}
在哪里初始化我的 components ?
我為我的功能的所有組件創建了一個單例 holder。這個 holder 用於創建,維護和銷毀我的 component 實例。
@Singleton
object PostDH {
private var listComponent: ListComponent? = null
fun listComponent(): ListComponent {
if (listComponent == null)
listComponent = DaggerListComponent.builder().coreComponent(CoreApp.coreComponent).build()
return listComponent as ListComponent
}
fun destroyListComponent() {
listComponent = null
}
}
注意:為了 Dagger 的注解能夠工作,不要忘記在你的 feature 模塊中增加下面依賴
kapt "com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:${versions.dagger}"
總結
盡管把你的單獨的 application 轉成模塊化有一些棘手,其中一些我試圖通過上面的方法來解決,優點是深刻的。如果您在模塊中遇到任何障礙,請隨時在下面提及它們,我們可以一起討論解決方案。
謝謝。
